Allele-specific suppression in Caenorhabditis elegans reveals details of EMS mutagenesis and a possible moonlighting interaction between the vesicular acetylcholine transporter and ERD2 receptors
- PMID: 33914877
- PMCID: PMC8664489
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyab065
Allele-specific suppression in Caenorhabditis elegans reveals details of EMS mutagenesis and a possible moonlighting interaction between the vesicular acetylcholine transporter and ERD2 receptors
Abstract
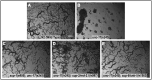
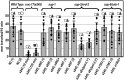
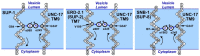
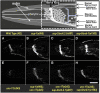
A missense mutant, unc-17(e245), which affects the Caenorhabditis elegans vesicular acetylcholine transporter UNC-17, has a severe uncoordinated phenotype, allowing efficient selection of dominant suppressors that revert this phenotype to wild-type. Such selections permitted isolation of numerous suppressors after EMS (ethyl methanesulfonate) mutagenesis, leading to demonstration of delays in mutation fixation after initial EMS treatment, as has been shown in T4 bacteriophage but not previously in eukaryotes. Three strong dominant extragenic suppressor loci have been defined, all of which act specifically on allele e245, which causes a G347R mutation in UNC-17. Two of the suppressors (sup-1 and sup-8/snb-1) have previously been shown to encode synaptic proteins able to interact directly with UNC-17. We found that the remaining suppressor, sup-2, corresponds to a mutation in erd-2.1, which encodes an endoplasmic reticulum retention protein; sup-2 causes a V186E missense mutation in transmembrane helix 7 of ERD-2.1. The same missense change introduced into the redundant paralogous gene erd-2.2 also suppressed unc-17(e245). Suppression presumably occurred by compensatory charge interactions between transmembrane helices of UNC-17 and ERD-2.1 or ERD-2.2, as previously proposed in work on suppression by SUP-1(G84E) or SUP-8(I97D)/synaptobrevin. erd-2.1(V186E) homozygotes were fully viable, but erd-2.1(V186E); erd-2.2(RNAi) exhibited synthetic lethality [like erd-2.1(RNAi); erd-2.2(RNAi)], indicating that the missense change in ERD-2.1 impairs its normal function in the secretory pathway but may allow it to adopt a novel moonlighting function as an unc-17 suppressor.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; EMS mutagenesis; KDEL receptor; acetylcholine transporter; genetic suppression; moonlighting; protein interaction; synapse.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Alfonso A, Grundahl K, Duerr JS, Han HP, Rand JB.. 1993. The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-17 gene: a putative vesicular acetylcholine transporter. Science. 261:617–619. - PubMed
-
- Bräuer P, Parker JL, Gerondopoulos A, Zimmermann I, Seeger MA, et al.2019. Structural basis for pH-dependent retrieval of ER proteins from the Golgi by the KDEL receptor. Science. 363:1103–1107. - PubMed
-
- C. elegans Sequencing Consortium 1998. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science. 282:2012–2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

