Complexation of maltodextrin-based inulin and green tea polyphenols via different ultrasonic pretreatment
- PMID: 33915483
- PMCID: PMC8093945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105568
Complexation of maltodextrin-based inulin and green tea polyphenols via different ultrasonic pretreatment
Abstract
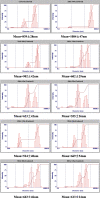
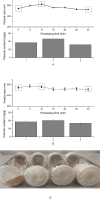
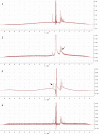
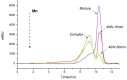
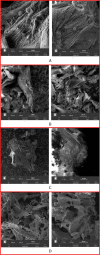
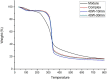
Ultrasound has been applied in food processing for various purpose, showing potential to advance the physical and chemical modification of natural compounds. In order to explore the effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on the complexation of inulin and tea polyphenols (TPP), different frequencies (25, 40, 80 kHz) and output power (40, 80, 120 W) were carried out. According to the comparison in particle size distribution and phenolic content of different inulin-TPP complexes, it was indicated that high-intensity ultrasonic (HIU) treatment (25 kHz, 40 W, 10 min) could accelerate the interaction of polysaccharides and polyphenols. Moreover, a series of spectral analysis including UV-Vis, FT-IR and NMR jointly evidenced the formation of hydrogen bond between saccharides and phenols. However, the primary structure of inulin and the polysaccharide skeleton were not altered by the combination. Referring to field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), the morphology of ultrasound treated-complex presented a slight agglomeration in the form of bent sheets, compared to non-treated sample. The inulin-TPP complex also revealed better stability based on thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Thus, it can be speculated from the identifications that proper ultrasonic treatment is promising to promote the complexation of some food components during processing.
Keywords: Complexation; Identification; Inulin; Tea polyphenols; Ultrasonic treatment.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Córdova A., Astudillo-Castro C., Ruby-Figueroa R., Valencia P., Soto C. Recent advances and perspectives of ultrasound assisted membrane food processing. Food Res. Int. 2020;133 - PubMed
-
- Paris J.L., Mannaris C., Cabañas M.V., Carlisle R., Manzano M., Vallet-Regí M., Coussios C.C. Ultrasound-mediated cavitation-enhanced extravasation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled-release drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2018;340:2–8.
-
- Wu . Springer; Netherlands: 2013. Advances in Ultrasound Technology for Environmental Remediation.
-
- Fu X., Belwal T., Cravotto G., Luo Z. Sono-physical and sono-chemical effects of ultrasound: primary applications in extraction and freezing operations and influence on food components. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019;104726 - PubMed
-
- Li S., Zhang R., Lei D., Huang Y., Cheng S., Zhu Z., Wu Z., Cravotto G. Impact of ultrasound, microwaves and high-pressure processing on food components and their interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;109:1–15.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

