Temporal patterns of nasal symptoms in patients with mild severity SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33915513
- PMCID: PMC8064817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103076
Temporal patterns of nasal symptoms in patients with mild severity SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
Background: No study to date has analyzed the progression of sinonasal symptoms over time in COVID-19 patients. The purpose of this study is to analyze the progression of sinonasal symptoms and risk factors for olfactory dysfunction in the mild severity COVID-19 patient.
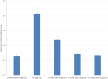
Methods: An internet survey was used to assess sinonasal symptoms in patients with COVID-19. Changes in rhinologic domain and symptom-specific Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22) scores were compared at five time points: two weeks before diagnosis, at diagnosis, two weeks after diagnosis, four weeks after diagnosis, and six months after diagnosis.
Results: 521 responses were collected. Rhinologic domain SNOT-22 scores increased significantly (p < 0.001) to 8.94 at the time of diagnosis, remained elevated two weeks post-diagnosis (5.14, p = 0.004), and decreased significantly four weeks post-diagnosis (3.14, p = 0.004). Smell-specific SNOT-22 scores peaked at the time of diagnosis (2.05, p < 0.001), remained elevated two weeks after diagnosis (1.19, p < 0.001), and returned to baseline four weeks post-diagnosis (0.64, p > 0.999). Taste-specific SNOT-22 scores also peaked at diagnosis (2.06, p < 0.001), remained elevated two weeks after diagnosis (1.19, p < 0.001), and returned to baseline four weeks after diagnosis (0.71, p > 0.999). There were no significant differences in sense of smell or taste between 1-month and 6-month timepoints.
Conclusion: Sinonasal symptoms, particularly loss of smell and taste, may be important presenting symptoms in the mild severity COVID-19 patient. Our findings support incorporating these symptoms into screening protocols.
Level of evidence: 4.
Keywords: Anosmia; COVID-19; SNOT-22.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Taste and Smell Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Aug 1;146(8):723-728. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1155. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32556070 Free PMC article.
-
Six-Month Psychophysical Evaluation of Olfactory Dysfunction in Patients with COVID-19.Chem Senses. 2021 Jan 1;46:bjab006. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjab006. Chem Senses. 2021. PMID: 33575808 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of effects of chronic nasal steroid use on rhinological symptoms of COVID-19 with SNOT-22 questionnaire.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Jun;73(3):781-785. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00235-1. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33625686 Free PMC article.
-
Smell and taste disorders in COVID-19: From pathogenesis to clinical features and outcomes.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Mar 23;748:135694. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135694. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33600902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sudden onset, acute loss of taste and smell in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review.Acta Odontol Scand. 2020 Aug;78(6):467-473. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2020.1787505. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Acta Odontol Scand. 2020. PMID: 32762282
Cited by
-
Intranasal Xylitol for the Treatment of COVID-19 in the Outpatient Setting: A Pilot Study.Cureus. 2022 Jul 23;14(7):e27182. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27182. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36039203 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, virological and immunological evolution of the olfactory and gustatory dysfunction in COVID-19.Am J Otolaryngol. 2022 Jan-Feb;43(1):103170. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103170. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Am J Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34391165 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory recovery following infection with COVID-19: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 9;16(11):e0259321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259321. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34752471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH . World Health Organization; 2020. WHO announces COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous