Magnetic Core-Shell Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Conjugates for Extraction of Antazoline and Hydroxyantazoline from Human Plasma-Material Characterization, Theoretical Analysis and Pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 33915912
- PMCID: PMC8038096
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073665
Magnetic Core-Shell Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Conjugates for Extraction of Antazoline and Hydroxyantazoline from Human Plasma-Material Characterization, Theoretical Analysis and Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
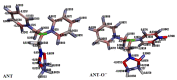
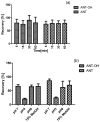
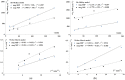
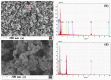
The aim of this study was to develop magnetic molecularly imprinted nano-conjugate sorbent for effective dispersive solid phase extraction of antazoline (ANT) and its metabolite, hydroxyantazoline (ANT-OH) in analytical method employing liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry method. The core-shell material was characterized in terms of adsorption properties, morphology and structure. The heterogeneous population of adsorption sites towards ANT-OH was characterized by two Kd and two Bmax values: Kd (1) = 0.319 µg L-1 and Bmax (1) = 0.240 μg g-1, and Kd (2) = 34.6 µg L-1 and Bmax (2) = 5.82 μg g-1. The elemental composition of magnetic sorbent was as follows: 17.55, 37.33, 9.14, 34.94 wt% for Si, C, Fe and O, respectively. The extraction protocol was optimized, and the obtained results were explained using theoretical analysis. Finally, the analytical method was validated prior to application to pharmacokinetic study in which the ANT was administrated intravenously to three healthy volunteers. The results prove that the novel sorbent could be useful in extraction of ANT and ANT-OH from human plasma and that the analytical strategy could be a versatile tool to explain a potential and pharmacological activity of ANT and ANT-OH.
Keywords: antazoline; atrial fibrillation; biomedical applications; core–shell nanostructures; dispersive solid phase extraction; hydroxyantazoline; magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers; mass spectrometry; particle characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Conjugates for Effective Extraction of Food Components-A Model Study of Tyramine Determination in Craft Beers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 3;22(17):9560. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179560. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502468 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a novel liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of antazoline in human plasma: Result of ELEPHANT-I [ELEctrophysiological, pharmacokinetic and hemodynamic effects of PHenazolinum (ANTazoline mesylate)] human pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 May 10;123:113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.01.060. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 26895496
-
Characterization of In Vitro and In Vivo Metabolism of Antazoline Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 18;21(24):9693. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249693. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33353167 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Component Ratio on Analytical Performance.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020;68(11):1013-1024. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00551. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 33132368 Review.
-
Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Bisphenols Extraction from Food Samples - A Review.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2020;50(4):311-321. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2019.1626698. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 31199164 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and characterization of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the rapid and selective determination of clofazimine in blood plasma samples.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 26;10(13):e33396. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33396. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040332 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Conjugates for Effective Extraction of Food Components-A Model Study of Tyramine Determination in Craft Beers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 3;22(17):9560. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179560. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502468 Free PMC article.
-
Recent molecularly imprinted polymers applications in bioanalysis.Chem Zvesti. 2023;77(2):619-655. doi: 10.1007/s11696-022-02488-3. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Chem Zvesti. 2023. PMID: 36213319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Performance Verification of the PBPK Model for Antazoline and Its Metabolite and Its Utilization for Pharmacological Hypotheses Formulating.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 20;15(3):379. doi: 10.3390/ph15030379. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crapnell R.D., Dempsey-Hibbert N.C., Peeters M., Tridente A., Banks C.E. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical biosensors: Overcoming the challenges of detecting vital biomarkers and speeding up diagnosis. Talanta Open. 2020;2:100018. doi: 10.1016/j.talo.2020.100018. - DOI
-
- Wackerlig J., Lieberzeit P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing—Synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015;207:144–157. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.094. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

