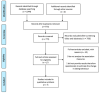
Consequences of the COVID-19 Syndemic for Nutritional Health: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33916087
- PMCID: PMC8065714
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13041168
Consequences of the COVID-19 Syndemic for Nutritional Health: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Confinement at home, quarantine, and social distancing are some measures adopted worldwide to prevent the spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2), which has been generating an important alteration in the routines and qualities of life of people. The impact on health is still being evaluated, and consequences in the nutritional field are not entirely clear. The study objective was to evaluate the current evidence about the impact that preventive measures of physical contact restriction causes in healthy nutrition. A systematic review was carried out according to the "Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses" PRISMA Group and Cochrane method for rapid systematic reviews. Searching was performed in six electronic databases and evaluated articles published between 2010 and 2020, including among their participants adult subjects who had been exposed to the preventive measures of physical contact restriction. Seven studies met the selection criteria and reported an overall increase in food consumption, weight, Body Mass Index (BMI), and a change in eating style. Findings suggest that healthy nutrition is affected by preventive measures to restrict physical contact as a result of the COVID-19 syndemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; confinement; eating behavior; feeding behavior; pandemic; quarantine; social distancing; social isolation; syndemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Did social isolation during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic have an impact on the lifestyles of citizens?Epidemiol Prev. 2020 Sep-Dec;44(5-6 Suppl 2):353-362. doi: 10.19191/EP20.5-6.S2.137. Epidemiol Prev. 2020. PMID: 33412829 English.
-
Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013574. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013574.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33959956 Free PMC article.
-
Social Distancing in Chronic Migraine during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Results from a Multicenter Observational Study.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 19;13(4):1361. doi: 10.3390/nu13041361. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33921674 Free PMC article.
-
Early public adherence with and support for stay-at-home COVID-19 mitigation strategies despite adverse life impact: a transnational cross-sectional survey study in the United States and Australia.BMC Public Health. 2021 Mar 15;21(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10410-x. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33722226 Free PMC article.
-
Travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 5;10:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMID: 33502002 Updated.
Cited by
-
Mapping the landscape and structure of global research on nutrition and COVID-19: visualization analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2022 Jun 10;41(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41043-022-00304-y. J Health Popul Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35689295 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of public health and social measures (PHSM) implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic: An overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Evid Synth Methods. 2024 Apr 29;2(5):e12055. doi: 10.1002/cesm.12055. eCollection 2024 May. Cochrane Evid Synth Methods. 2024. PMID: 40476261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eating habits of children and adolescents during the COVID-19 era: A systematic review.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 18;9:1004953. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1004953. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36330134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMI Increases in Individuals with COVID-19-Associated Olfactory Dysfunction.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 26;15(21):4538. doi: 10.3390/nu15214538. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960191 Free PMC article.
-
Assuring Healthy Populations During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Recognizing Women's Contributions in Addressing Syndemic Interactions.Front Public Health. 2022 May 27;10:856932. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.856932. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35712273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde Folha Informativa COVID-19-Escritório da OPAS e da OMS no Brasil. [(accessed on 10 January 2020)]; Available online: https://www.paho.org/pt/covid19.
-
- Ammar A., Chtourou H., Boukhris O., Trabelsi K., Masmoudi L., Brach M., Bouaziz B., Bentlage E., How D., Ahmed M., et al. Social participation and life satisfaction of peoples during the COVID-19 home confinement: The ECLB-COVID19 mul-ticenter study. [(accessed on 18 February 2021)];MedRxiv. 2020 5 Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.05.20091066v1. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Novel Coronavirus (2019-Ncov) Advice for the Public. [(accessed on 1 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-f....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous