Beneficial Role of Carica papaya Extracts and Phytochemicals on Oxidative Stress and Related Diseases: A Mini Review
- PMID: 33916114
- PMCID: PMC8066973
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10040287
Beneficial Role of Carica papaya Extracts and Phytochemicals on Oxidative Stress and Related Diseases: A Mini Review
Abstract
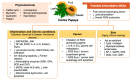
Oxidative stress is a result of disruption in the balance between antioxidants and pro-oxidants in which subsequently impacting on redox signaling, causing cell and tissue damages. It leads to a range of medical conditions including inflammation, skin aging, impaired wound healing, chronic diseases and cancers but these conditions can be managed properly with the aid of antioxidants. This review features various studies to provide an overview on how Carica papaya help counteract oxidative stress via various mechanisms of action closely related to its antioxidant properties and eventually improving the management of various oxidative stress-related health conditions. Carica papaya is a topical plant species discovered to contain high amounts of natural antioxidants that can usually be found in their leaves, fruits and seeds. It contains various chemical compounds demonstrate significant antioxidant properties including caffeic acid, myricetin, rutin, quercetin, α-tocopherol, papain, benzyl isothiocyanate (BiTC), and kaempferol. Therefore, it can counteract pro-oxidants via a number of signaling pathways that either promote the expression of antioxidant enzymes or reduce ROS production. These signaling pathways activate the antioxidant defense mechanisms that protect the body against both intrinsic and extrinsic oxidative stress. To conclude, Carica papaya can be incorporated into medications or supplements to help manage the health conditions driven by oxidative stress and further studies are needed to investigate the potential of its chemical components to manage various chronic diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Carica papaya; aging; antioxidant; cancer; diabetes; inflammation; oxidative stress; periodontal disease; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolomic profiling of the phytomedicinal constituents of Carica papaya L. leaves and seeds by 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate statistical analysis.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015 Nov 10;115:74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.06.035. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015. PMID: 26163870
-
Nutraceutical Potential of Carica papaya in Metabolic Syndrome.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 16;11(7):1608. doi: 10.3390/nu11071608. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31315213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracts of Mauritian Carica papaya (var. solo) protect SW872 and HepG2 cells against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress.J Food Sci Technol. 2017 Jun;54(7):1917-1927. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2626-4. Epub 2017 Apr 28. J Food Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28720948 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Efficacy of Topical Carica papaya Leaf Extract and Hemocoagulase in Postoperative Wound Healing After Therapeutic Orthodontic Premolar Extractions: a Split Mouth Study.Cureus. 2024 Jun 8;16(6):e61946. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61946. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38978880 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of Carica papaya.J Immunotoxicol. 2016 Jul;13(4):590-602. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2016.1149528. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Immunotoxicol. 2016. PMID: 27416522 Review.
Cited by
-
Papain Suppresses Atopic Skin Inflammation through Anti-Inflammatory Activities Using In Vitro and In Vivo Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 30;13(8):928. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080928. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199175 Free PMC article.
-
Plant ingredients in Thai food: a well-rounded diet for natural bioactive associated with medicinal properties.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 1;11:e14568. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14568. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36879911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Experimental Bleaching Gels With Enzymes on Composite and Enamel.Int Dent J. 2025 Apr;75(2):1234-1245. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.08.014. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39266399 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of phytofabricated silver nanoparticles using Carica papaya L. against Gram-negative bacteria.Vet World. 2023 Jun;16(6):1301-1311. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2023.1301-1311. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Vet World. 2023. PMID: 37577189 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the bioactive compounds of Carica papaya leaves: phytol's role in combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 7;15:1564787. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1564787. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40692687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aradhya M.K., Manshardt R.M., Zee F., Morden C.W. A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Carica, L. (Caricaceae) based on restriction fragment length variation in a cpDNA intergenic spacer region. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1999;46:579–586. doi: 10.1023/A:1008786531609. - DOI
-
- Yogiraj V., Goyal P., Chauhan C.S., Goyal A., Vyas B. Carica papaya Linn: An overview. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2014;2:1–8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources