Clinical Activity of an hTERT-Specific Cancer Vaccine (Vx-001) in "Immune Desert" NSCLC
- PMID: 33916194
- PMCID: PMC8037524
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071658
Clinical Activity of an hTERT-Specific Cancer Vaccine (Vx-001) in "Immune Desert" NSCLC
Abstract
Background: Tumors can be separated into immunogenic/hot and non-immunogenic/cold on the basis of the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), the expression of PD-L1 and the tumor mutation burden (TMB). In immunogenic tumors, TILs become unable to control tumor growth because their activity is suppressed by different inhibitory pathways, including PD-1/PD-L1. We hypothesized that tumor vaccines may not be active in the immunosuppressive microenvironment of immunogenic/hot tumors while they could be efficient in the immune naïve microenvironment of non-immunogenic/cold tumors.
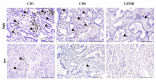
Methods: The randomized phase II Vx-001-201 study investigated the effect of the Vx-001 vaccine as maintenance treatment in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Biopsies from 131 (68 placebo and 63 Vx-001) patients were retrospectively analyzed for PD-L1 expression and TIL infiltration. TILs were measured as tumor-associated immune cells (TAICs), CD3-TILs, CD8-TILs and granzyme B-producing TILs (GZMB-TILs). Patients were distinguished into PD-L1(+) and PD-L1(-) and into TIL high and TIL low.
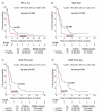
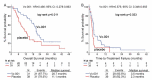
Findings: There was no correlation between PD-L1 expression and Vx-001 clinical activity. In contrast, Vx-001 showed a significant improvement of overall survival (OS) vs. placebo in TAIC low (21 vs. 8.1 months, p = 0.003, HR = 0.404, 95% CI 0.219-0.745), CD3-TIL low (21.6 vs. 6.6 months, p < 0.001, HR = 0.279, 95% CI 0.131-0.595), CD8-TIL low (21 vs. 6.6 months, p < 0.001; HR = 0.240, 95% CI 0.11-0.522) and GZMB-TIL low (20.7 vs. 11.1 months, p = 0.011, HR = 0.490, 95% CI 0.278-0.863). Vx-001 did not offer any clinical benefit in patients with TAIC high, CD3-TIL high, CD8-TIL high or GZMB-TIL high tumors. CD3-TIL, CD8-TIL and GZMB-TIL were independent predictive factors of Vx-001 efficacy.
Conclusions: These results support the hypothesis that Vx-001 may be efficient in patients with non-immunogenic/cold but not with immunogenic/hot tumors.
Keywords: Vx-001; cancer vaccines; granzyme B; immunologically cold tumors; metastatic non-small cell lung cancer; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. J.M.-J. is an employee and shareholder of Vaxon Biotech. K.K. and J.P.K. are shareholders of Vaxon Biotech. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Cibotti R., Kanellopoulos J.M., Cabaniols J.P., Halle-Panenko O., Kosmatopoulos K., Sercarz E., Kourilsky P. Tolerance to a self-protein involves its immunodominant but does not involve its subdominant determinants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1992;89:416–420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.416. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gross D.A., Graff-Dubois S., Opolon P., Cornet S., Alves P., Bennaceur-Griscelli A., Faure O., Guillaume P., Firat H., Chouaib S., et al. High vaccination efficiency of low-affinity epitopes in antitumor immunotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2004;113:425–433. doi: 10.1172/JCI200419418. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scardino A., Gross D.A., Alves P., Schultze J.L., Graff-Dubois S., Faure O., Tourdot S., Chouaib S., Nadler L.M., Lemonnier F.A., et al. HER-2/neu and hTERT cryptic epitopes as novel targets for broad spectrum tumor immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2002;168:5900–5906. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5900. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vetsika E.K., Konsolakis G., Aggouraki D., Kotsakis A., Papadimitraki E., Christou S., Menez-Jamet J., Kosmatopoulos K., Georgoulias V., Mavroudis D. Immunological responses in cancer patients after vaccination with the therapeutic telomerase-specific vaccine Vx-001. Cancer immunol. Immunotherapy. 2012;61:157–168. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

