Antioxidant Adjustments of Olive Trees (Olea Europaea) under Field Stress Conditions
- PMID: 33916326
- PMCID: PMC8066335
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10040684
Antioxidant Adjustments of Olive Trees (Olea Europaea) under Field Stress Conditions
Abstract
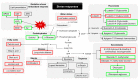
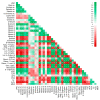
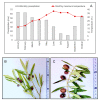
Extreme climate events are increasingly frequent, and the 2017 summer was particularly critical in the Mediterranean region. Olive is one of the most important species of this region, and these climatic events represent a threat to this culture. However, it remains unclear how olive trees adjust the antioxidant enzymatic system and modulate the metabolite profile under field stress conditions. Leaves from two distinct adjacent areas of an olive orchard, one dry and the other hydrated, were harvested. Tree water status, oxidative stress, antioxidant enzymes, and phenolic and lipophilic metabolite profiles were analyzed. The environmental conditions of the 2017 summer caused a water deficit in olive trees of the dry area, and this low leaf water availability was correlated with the reduction of long-chain alkanes and fatty acids. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide radical (O2•-) levels increased in the trees collected from the dry area, but lipid peroxidation did not augment. The antioxidant response was predominantly marked by guaiacol peroxidase (GPOX) activity that regulates the H2O2 harmful effect and by the action of flavonoids (luteolin-7-O-glucuronide) that may act as reactive oxygen species scavengers. Secoiridoids adjustments may also contribute to stress regulation. This work highlights for the first time the protective role of some metabolite in olive trees under field drought conditions.
Keywords: Olea europaea; climate change; drought; flavonoids; rainfed olive groves; secoiridoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- FAOSTAT Production Share of Olives by Region for 2017. [(accessed on 4 January 2021)]; Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize.
-
- IPCC . In: Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change. Masson-Delmotte V., Zhai P.H.-O., Pörtner D., Roberts J., Skea P.R., Shukla A., Pirani W., Moufouma-Okia C., Péan R., Pidcock S., et al., editors. IPCC; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018.
-
- Fernández J.E., Diaz-Espejo A., Romero R., Hernandez-Santana V., García J.M., Padilla-Díaz C.M., Cuevas M.V. Precision Irrigation in Olive (Olea europaea L.) Tree Orchards. Water Scarcity Sustain. Agric. Semiarid Environ. 2018:179–217. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-813164-0.00009-0. - DOI
-
- Araújo M., de Oliveira J.M.P.F., Santos C., Moutinho-Pereira J., Correia C., Dias M.C. Responses of olive plants exposed to different irrigation treatments in combination with heat shock: Physiological and molecular mechanisms during exposure and recovery. Planta. 2019;249:1583–1598. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03109-2. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

