Human Somatostatin SST4 Receptor Transgenic Mice: Construction and Brain Expression Pattern Characterization
- PMID: 33916620
- PMCID: PMC8038480
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073758
Human Somatostatin SST4 Receptor Transgenic Mice: Construction and Brain Expression Pattern Characterization
Abstract
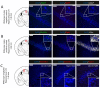
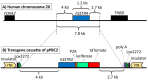
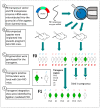
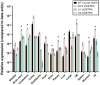
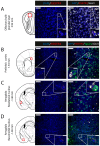
Somatostatin receptor subtype 4 (SST4) has been shown to mediate analgesic, antidepressant and anti-inflammatory functions without endocrine actions; therefore, it is proposed to be a novel target for drug development. To overcome the species differences of SST4 receptor expression and function between humans and mice, we generated an SST4 humanized mouse line to serve as a translational animal model for preclinical research. A transposon vector containing the hSSTR4 and reporter gene construct driven by the hSSTR4 regulatory elements were created. The vector was randomly inserted in Sstr4-deficient mice. hSSTR4 expression was detected by bioluminescent in vivo imaging of the luciferase reporter predominantly in the brain. RT-qPCR confirmed the expression of the human gene in the brain and various peripheral tissues consistent with the in vivo imaging. RNAscope in situ hybridization revealed the presence of hSSTR4 transcripts in glutamatergic excitatory neurons in the CA1 and CA2 regions of the hippocampus; in the GABAergic interneurons in the granular layer of the olfactory bulb and in both types of neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex, piriform cortex, prelimbic cortex and amygdala. This novel SST4 humanized mouse line might enable us to investigate the differences of human and mouse SST4 receptor expression and function and assess the effects of SST4 receptor agonist drug candidates.
Keywords: PiggyBac (PB) transposon vector; RNAscope in situ hybridization; SSTR4 humanized mice; Sstr4 KO mice; ligation-mediated PCR; somatostatin.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest. Z.H. and E.P. are the founders of PharmInVivo Ltd., Pécs, Hungary. Z.H. and E.P. are stakeholders of ALGONIST Biotechnologies GmbH, Wien, Austria. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Helyes Z., Pinter E., Sandor K., Elekes K., Banvolgyi A., Keszthelyi D., Szoke E., Toth D.M., Sandor Z., Kereskai L., et al. Impaired Defense Mechanism against Inflammation, Hyperalgesia, and Airway Hyperreactivity in Somatostatin 4 Receptor Gene-Deleted Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:13088–13093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900681106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- National Brain Research Program 2017-1.2.1-NKP-2017-00002/Hungarian Government
- GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00050/Hungarian Government
- EFOP 3.6.2-17-2017-00008 N/Hungarian Government
- EFOP-3.6.1-16-2016-00004/Hungarian Government
- EFOP-3.6.2-16-2017-00006/Hungarian Government
- FIKPII-17886-4/23018/FEKUTSTRAT/Hungarian Government
- NKFIH-OTKA-K 134214/Hungarian Government
- János Bolyai Research Scholarship/Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- Talentum Fundation Scholarship/Gedeon Richter Plc.
- Research grant of Medical School, University of Pécs (KA-2019-12)/Hungarian Government
- ÚNKP-20-4-II-PTE-874/Hungarian Government
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

