Alignment of Physical Activity in Older Couples Affected by Osteoarthritis: Investigation by Accelerometry and Questionnaire
- PMID: 33917622
- PMCID: PMC8038764
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071544
Alignment of Physical Activity in Older Couples Affected by Osteoarthritis: Investigation by Accelerometry and Questionnaire
Abstract
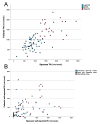
This study examined whether an alignment of physical activity (PA) between osteoarthritis patients and their spouses, which was previously proven by accelerometry, might also be revealed by self-report. The PA of 28 cohabitating couples (58-83 years) was assessed by means of synchronous accelerometry (ActiGraph wGTX3-BT) and compared to their according self-reports in the German Physical Activity, Exercise, and Sport Questionnaire (BSA-F). Both methods were used to quantify the average weekly light PA, moderate to vigorous PA (MVPA), and total PA. Accelerometry revealed no differences in weekly light PA and total PA (p ≥ 0.187) between patients and spouses, whereas the patients' spouses accumulated significantly more MVPA (p = 0.015). In contrast, the self-report did not reveal any differences between the two groups in terms of PA (p ≥ 0.572). Subsequent correlation analyses indicated that accelerometry data for mild PA and total PA were significantly correlated in couples (r ≥ 0.385, p ≤ 0.024), but MVPA was not (r = 0.257, p = 0.097). The self-reported PA data, on the other hand, did not indicate any significant correlation (r ≤ 0.046, p ≥ 0.409). The presented results give a first indication that an alignment of PA between osteoarthritis patients and their spouses is most likely to be detected by accelerometry, but not by self-report.
Keywords: assessment; behavioral alignment; older couples; osteoarthritis; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral Conformity of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Older Couples with One Partner Suffering from End-Stage Osteoarthritis.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Jan 17;15:61-74. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S222490. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 32021134 Free PMC article.
-
Domain-Specific Self-Reported and Objectively Measured Physical Activity in Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Mar 1;14(3):242. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030242. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28257046 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerometer-Measured Versus Self-Reported Physical Activity Levels and Sedentary Behavior in Women Before and 9 Months After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass.Obes Surg. 2016 Jul;26(7):1463-70. doi: 10.1007/s11695-015-1971-5. Obes Surg. 2016. PMID: 26613756
-
The association of the neighbourhood built environment with objectively measured physical activity in older adults with and without lower limb osteoarthritis.BMC Public Health. 2016 Aug 3;15:710. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3347-8. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27488608 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerometer-derived physical activity analysis of elderly osteoarthritis patients.Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2023 Aug;66:102808. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2023.102808. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2023. PMID: 37352763
Cited by
-
Active With Whom? Examining the Social Context of Physical Activity in Individuals After Stroke and Their Partners.Front Public Health. 2021 Sep 29;9:754046. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.754046. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34660523 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

