N-3 PUFA Prevent Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Beta-Amyloid-Induced Toxicity
- PMID: 33917814
- PMCID: PMC8068120
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14040339
N-3 PUFA Prevent Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Beta-Amyloid-Induced Toxicity
Abstract
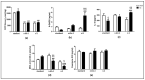
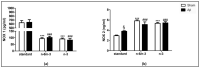
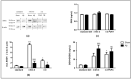
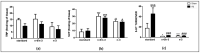
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are involved in brain disorders associated to amyloid beta (Aβ) toxicity for which oxidative stress, neurochemical dysfunctions, and neuroinflammation are underlying mechanisms. Here, mechanisms through which lifelong exposure to n-3 PUFA-enriched or n-6/n-3 balanced diets could elicit a protective role in a rat model of Aβ-induced toxicity were investigated. To this aim, we quantified hippocampal reactive oxygen species (ROS) amount, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine and interleukin-10 levels, NADPH oxidase (NOX) 1, NOX2, superoxide dismutase 1, and glutathione contents, as well as plasmatic malondialdehyde. Moreover, in the same experimental groups, we assessed tryptophan, serotonin, and its turnover, kynurenine, and noradrenaline amounts. Results showed increased hippocampal ROS and NOX2 levels, serotonin turnover, kynurenine, and noradrenaline contents in Aβ-treated rats. Both n-6/n-3 balanced and n-3 PUFA enriched diets reduced ROS production, NOX1 and malondialdehyde levels, serotonin turnover, and kynurenine amount in Aβ-injected rats, while increasing NOX2, superoxide dismutase 1, and serotonin contents. No differences in plasmatic coenzyme Q10, reduced glutathione (GSH) and tryptophan levels were detected among different experimental groups, whereas GSH + oxidized glutathione (GSSG) levels were increased in sham animals fed with n-3 PUFA enriched diet and in Aβ-treated rats exposed to both n-6/n-3 balanced and n-3 enriched diets. In addition, Aβ-induced decrease of interleukin-10 levels was prevented by n-6/n-3 PUFA balanced diet. N-3 PUFA enriched diet further increased interleukin-10 and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels. In conclusion, our data highlight the possible neuroprotective role of n-3 PUFA in perturbation of oxidative equilibrium induced by Aβ-administration.
Keywords: beta-amyloid; inflammation; n-3 PUFA; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depressive-like phenotype evoked by lifelong nutritional omega-3 deficiency in female rats: Crosstalk among kynurenine, Toll-like receptors and amyloid beta oligomers.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul;87:444-454. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.01.015. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 31987923
-
N-3 PUFA diet enrichment prevents amyloid beta-induced depressive-like phenotype.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Mar;129:526-534. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.034. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29203442
-
Effects of n-3 PUFA enriched and n-3 PUFA deficient diets in naïve and Aβ-treated female rats.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:326-335. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30028991
-
Fatty acids, the immune response, and autoimmunity: a question of n-6 essentiality and the balance between n-6 and n-3.Lipids. 2003 Apr;38(4):323-41. doi: 10.1007/s11745-003-1067-z. Lipids. 2003. PMID: 12848277 Review.
-
Amyloid beta-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. A review.Free Radic Res. 2002 Dec;36(12):1307-13. doi: 10.1080/1071576021000049890. Free Radic Res. 2002. PMID: 12607822 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods in Mitigating Cellular Senescence and Its Related Aspects: A Key Strategy for Delaying or Preventing Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Nutrients. 2025 May 28;17(11):1837. doi: 10.3390/nu17111837. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Very-Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Central Nervous System and Their Potential Benefits for Treating Alcohol Use Disorder: Reviewing Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):2993. doi: 10.3390/nu15132993. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Medicine in Alzheimer's Disease: Investigating Comorbid Common Biological Substrates in the Rat Model of Amyloid Beta-Induced Toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:799561. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.799561. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046821 Free PMC article.
-
Glucoraphanin Triggers Rapid Antidepressant Responses in a Rat Model of Beta Amyloid-Induced Depressive-like Behaviour.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;15(9):1054. doi: 10.3390/ph15091054. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145275 Free PMC article.
-
Potential therapeutic effects and pharmacological evidence of sinomenine in central nervous system disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 16;13:1015035. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015035. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

