Contribution of Pro-Inflammatory Molecules Induced by Respiratory Virus Infections to Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 33917837
- PMCID: PMC8068239
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14040340
Contribution of Pro-Inflammatory Molecules Induced by Respiratory Virus Infections to Neurological Disorders
Abstract
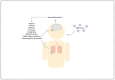
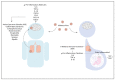
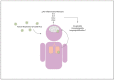
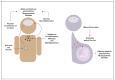
Neurobehavioral alterations and cognitive impairment are common phenomena that represent neuropsychiatric disorders and can be triggered by an exacerbated immune response against pathogens, brain injury, or autoimmune diseases. Pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and chemokines, are produced in the brain by resident cells, mainly by microglia and astrocytes. Brain infiltrating immune cells constitutes another source of these molecules, contributing to an impaired neurological synapse function, affecting typical neurobehavioral and cognitive performance. Currently, there is increasing evidence supporting the notion that behavioral alterations and cognitive impairment can be associated with respiratory viral infections, such as human respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and SARS-COV-2, which are responsible for endemic, epidemic, or pandemic outbreak mainly in the winter season. This article will review the brain's pro-inflammatory response due to infection by three highly contagious respiratory viruses that are the leading cause of acute respiratory illness, morbidity, and mobility in infants, immunocompromised and elderly population. How these respiratory viral pathogens induce increased secretion of pro-inflammatory molecules and their relationship with the alterations at a behavioral and cognitive level will be discussed.
Keywords: brain; neuropsychiatric disorders; pro-inflammatory molecules; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type I astrocytes and microglia induce a cytokine response in an encephalitic murine coronavirus infection.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Aug;115:104474. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104474. Epub 2020 May 23. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32454103 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant T cell immunity triggered by human Respiratory Syncytial Virus and human Metapneumovirus infection.Virulence. 2017 Aug 18;8(6):685-704. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1265725. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 27911218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Causes and Long-Term Consequences of Viral Encephalitis.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 30;15:755875. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.755875. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34916908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2, which induces COVID-19, causes kawasaki-like disease in children: role of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 May-June,;34(3):767-773. doi: 10.23812/EDITORIAL-RONCONI-E-59. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 32476380
-
Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: a promising inhibitory strategy.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Nov-Dec;34(6):1971-1975. doi: 10.23812/20-1-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 33016027
Cited by
-
Cytokines in the Brain and Neuroinflammation: We Didn't Starve the Fire!Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 25;15(2):140. doi: 10.3390/ph15020140. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H7N7 viral infection elicits pronounced, sex-specific neuroinflammatory responses in vitro.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Aug 7;18:1444876. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1444876. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39171200 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological Impact of Respiratory Viruses: Insights into Glial Cell Responses in the Central Nervous System.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 20;12(8):1713. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081713. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of severe influenza as a risk factor for febrile seizures in children: a retrospective analysis.Front Pediatr. 2024 Oct 23;12:1418499. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1418499. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39507495 Free PMC article.
-
Viral infections in pregnancy and impact on offspring neurodevelopment: mechanisms and lessons learned.Pediatr Res. 2024 Jul;96(1):64-72. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03145-z. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38509227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cavaillon J.M. Pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokines: Myth or reality. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2001;47:695–702. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

