Purification and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Papain Inhibitor from Moringa oleifera with Antimicrobial and Anticoagulant Properties
- PMID: 33917878
- PMCID: PMC8068210
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040512
Purification and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Papain Inhibitor from Moringa oleifera with Antimicrobial and Anticoagulant Properties
Abstract
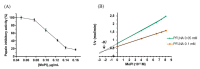
Plant cystatins (or phytocystatins) comprise a large superfamily of natural bioactive small proteins that typically act as protein inhibitors of papain-like cysteine proteases. In this report, we present the purification and characterization of the first phytocystatin isolated from Moringa oleifera (MoPI). MoPI has a molecular mass of 19 kDa and showed an extraordinary physicochemical stability against acidic pHs and high temperatures. Our findings also revealed that MoPI is one of the most potent cysteine protease inhibitors reported to date, with Ki and IC50 values of 2.1 nM and 5.7 nM, respectively. More interestingly, MoPI presents a strong antimicrobial activity against human pathogens such as Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, MoPI also showed important anticoagulant activity, which is an unprecedented property for this family of protease inhibitors. These results highlight the pharmaceutical potential of this plant and its derived bioactive molecules.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; antibacterial; anticoagulant; bioactive compound; papain inhibitor; phytocystatin; plant protease inhibitor; protease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Santos A., Luz L., Pontual E., Napoleão T., Paiva P., Coelho L. Moringa oleifera: Resource Management and Multiuse Life Tree. Adv. Res. 2015;4:388–402. doi: 10.9734/AIR/2015/18177. - DOI
-
- Gopalakrishnan L., Doriya K., Kumar D.S. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2016;5:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2016.04.001. - DOI
-
- Bancessi A., Pinto M.M.F., Duarte E., Catarino L., Nazareth T. The antimicrobial properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. for water treatment: A systematic review. SN Appl. Sci. 2020;2:323. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2142-4. - DOI
-
- Ma Z., Ahmad J., Zhang H., Khan I., Muhammad S. Evaluation of phytochemical and medicinal properties of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) as a potential functional food. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020;129:40–46. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2018.12.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

