Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition
- PMID: 33918360
- PMCID: PMC8066826
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13041180
Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition
Abstract
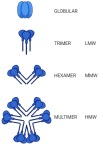
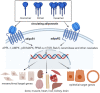
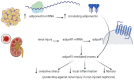
Adiponectin (a protein consisting of 244 amino acids and characterized by a molecular weight of 28 kDa) is a cytokine that is secreted from adipose tissues (adipokine). Available evidence suggests that adiponectin is involved in a variety of physiological functions, molecular and cellular events, including lipid metabolism, energy regulation, immune response and inflammation, and insulin sensitivity. It has a protective effect on neurons and neural stem cells. Adiponectin levels have been reported to be negatively correlated with cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and shown to be affected (i.e., significantly increased) by proper healthy nutrition. The present review comprehensively overviews the role of adiponectin in a range of diseases, showing that it can be used as a biomarker for diagnosing these disorders as well as a target for monitoring the effectiveness of preventive and treatment interventions.
Keywords: adipokine; adiponectin; adipose tissues; biomarker; cancer; disease; nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim D.H., Vanella L., Inoue K., Burgess A., Gotlinger K., Manthati V.L., Koduru S.R., Zeldin D.C., Falck J.R., Schwartzman M.L., et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid agonist regulates human mesenchymal stem cell-derived adipocytes through activation of HO-1-pAKT signaling and a decrease in PPARgamma. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19:1863–1873. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schondorf T., Maiworm A., Emmison N., Forst T., Pfutzner A. Biological background and role of adiponectin as marker for insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk. Clin. Lab. 2005;51:489–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

