Parenchymal Sparing Resection: Options in Duodenal and Pancreatic Surgery
- PMID: 33918376
- PMCID: PMC8038287
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071479
Parenchymal Sparing Resection: Options in Duodenal and Pancreatic Surgery
Abstract
Parenchymal sparing duodenal and pancreatic resection are safe procedures in selected patients with the aim to reduce endocrine and exocrine long-term dysfunction. When the tumor is benign or borderline malignant, this appears to be a good option for the surgeon, associated with low rates of severe surgery-related early postoperative complications and low in-hospital mortality. This mini review offers comments, tips and tricks, and a review of literature concerning those different options with specific illustrations in order to clarify their indication.
Keywords: ampullectomy; central-pancreatectomy; duodenectomy; enucleation; long-term functional outcomes; pancreatectomy; pancreatic sparing surgery; pancreatic tumor; uncus resection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


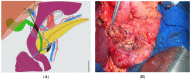
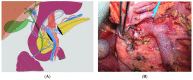
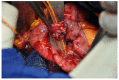

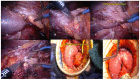
References
-
- Pea A., Tanno L., Nykänen T., Prasad P., Tunçer C., Robinson S., Marchegiani G. Comparison of Oncological and Surgical Outcomes Between Formal Pancreatic Resections and Parenchyma-Sparing Resections for Small PanNETs (<2 Cm): Pancreas2000 Research and Educational Program (Course 9) Study Protocol. Front. Med. 2020;7:559. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00559. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mintziras I., Keck T., Werner J., Fichtner-Feigl S., Wittel U., Senninger N., Vowinkel T., Köninger J., Anthuber M., Geißler B., et al. Indications for Resection and Perioperative Outcomes of Surgery for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Germany: An Analysis of the Prospective DGAV StuDoQ|Pancreas Registry. Surg. Today. 2019;49:1013–1021. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01838-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Centonze L., Di Sandro S., Lauterio A., De Carlis R., Botta F., Mariani A., Bagnardi V., De Carlis L. The Impact of Sarcopenia on Postoperative Course following Pancreatoduodenectomy: Single-Center Experience of 110 Consecutive Cases. Dig. Surg. 2020;37:312–320. doi: 10.1159/000504703. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

