Body Mass Index Reduction and Selected Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33918454
- PMCID: PMC8038293
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10071485
Body Mass Index Reduction and Selected Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Meta-Analysis
Abstract
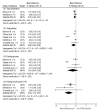
Although clinical studies have been carried out on the effects of weight reduction in sleep apnea patients, no direct link has been shown between weight reduction and changes in cardio-metabolic risk factors. We aimed to analyze changes in the apnea-hypopnea index and selected cardio-metabolic parameters (total cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose, insulin, blood pressure) in relation to the reduction in body mass index in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Medline, Web of Science and Cochrane databases were searched to combine results from individual studies in a single meta-analysis. We identified 333 relevant articles, from which 30 papers were assigned for full-text review, and finally 10 (seven randomized controlled trials and three nonrandomized studies) were included for data analysis. One unit of body mass index reduction was found to significantly influence changes in the apnea-hypopnea index (-2.83/h; 95% CI: -4.24, -1.41), total cholesterol (-0.12 mmol/L; 95% CI: -0.22, -0.01), triglycerides (-0.24 mmol/L; 95% CI: -0.46, -0.02), fasting insulin (-7.3 pmol/L; 95% CI: -11.5, -3.1), systolic (-1.86 mmHg; 95% CI: -3.57, -0.15) and diastolic blood pressure (-2.07 mmHg; 95% CI: -3.79, -0.35). Practical application of lifestyle modification resulting in the reduction of one unit of body mass index gives meaningful changes in selected cardio-metabolic risk factors in obstructive sleep apnea patients.
Keywords: apnea–hypopnea index; biological markers; blood pressure; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Foster G.D., Borradaile K.E., Sanders M.H., Millman R., Zammit G., Newman A.B., Wadden T.A., Kelley D., Wing R.R., Kuna S.T., et al. A randomized study on the effect of weight loss on obstructive sleep apnea among obese patients with type 2 diabetes: The Sleep AHEAD study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009;169:1619–1626. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.266. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomasouli M.-A., Brady E.M., Davies M.J., Hall A.P., Khunti K., Morris D.H., Gray L.J. The impact of diet and lifestyle management strategies for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Breath. 2013;17:925–935. doi: 10.1007/s11325-013-0806-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

