Morphometric Analysis of Brain in Newborn with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- PMID: 33918479
- PMCID: PMC8065764
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11040455
Morphometric Analysis of Brain in Newborn with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Abstract
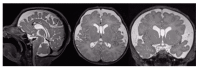
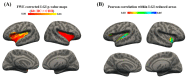
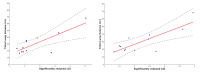
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a severe pediatric disorder with herniation of abdominal viscera into the thoracic cavity. Since neurodevelopmental impairment constitutes a common outcome, we performed morphometric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analysis on CDH infants to investigate cortical parameters such as cortical thickness (CT) and local gyrification index (LGI). By assessing CT and LGI distributions and their correlations with variables which might have an impact on oxygen delivery (total lung volume, TLV), we aimed to detect how altered perfusion affects cortical development in CDH. A group of CDH patients received both prenatal (i.e., fetal stage) and postnatal MRI. From postnatal high-resolution T2-weighted images, mean CT and LGI distributions of 16 CDH were computed and statistically compared to those of 13 controls. Moreover, TLV measures obtained from fetal MRI were further correlated to LGI. Compared to controls, CDH infants exhibited areas of hypogiria within bilateral fronto-temporo-parietal labels, while no differences were found for CT. LGI significantly correlated with TLV within bilateral temporal lobes and left frontal lobe, involving language- and auditory-related brain areas. Although the causes of neurodevelopmental impairment in CDH are still unclear, our results may suggest their link with altered cortical maturation and possible impaired oxygen perfusion.
Keywords: congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH); cortical thickness (CT); local gyrification index (LGI); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); total lung volume (TLV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Clark R.H., Hardin W.D., Hirschl R.B., Jaksic T., Lally K.P., Langham M.R., Wilson J.M. Current surgical management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: A report from the congenital diaphragmatic hernia study group. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1998;33:1004–1009. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3468(98)90522-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Danzer E., Gerdes M., D’Agostino J.A., Bernbaum J., Hoffman C., Herkert L., Rintoul N.E., Peranteau W.H., Flake A.W., Adzick N.S., et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at one year of age in congenital diaphragmatic hernia infants not treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015;50:898–903. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.03.040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

