Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Advanced Glycation End Products as Mediators and Markers of Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 33918767
- PMCID: PMC8068965
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9040405
Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Advanced Glycation End Products as Mediators and Markers of Oxidative Stress
Abstract
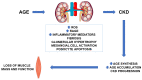
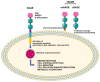
Sarcopenia is common in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and it is independently associated with morbidity and mortality. Advanced glycation end products (AGE) are mainly known as aging products. In CKD, AGE accumulate due to increased production and reduced kidney excretion. The imbalance between oxidant/antioxidant capacities in CKD patients is one of the main factors leading to AGE synthesis. AGE can, in turn, promote CKD progression and CKD-related complications by increasing reactive oxygen species generation, inducing inflammation, and promoting fibrosis. All these derangements can further increase AGE and uremic toxin accumulation and promote loss of muscle mass and function. Since the link between AGE and sarcopenia in CKD is far from being fully understood, we revised hereby the data supporting the potential contribution of AGE as mediators of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of sarcopenia. Understanding how AGE and oxidative stress impact the onset of sarcopenia in CKD may help to identify new potential markers of disease progression and/or therapeutic targets.
Keywords: advanced glycation end products (AGE); chronic kidney disease; oxidative stress; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Esposito K., Chiodini P., Ceriello A., Giugliano D. A nomogram to estimate the proportion of patients at hemoglobin A1c target <7% with noninsulin antidiabetic drugs in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of 137 randomized controlled trials with 39,845 patients. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51:305–311. doi: 10.1007/s00592-012-0370-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pereira R.A., Cordeiro A.C., Avesani C.M., Carrero J.J., Lindholm B., Amparo F.C., Amodeo C., Cuppari L., Kamimura M.A. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease on conservative therapy: Prevalence and association with mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015;30:1718–1725. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv133. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanatani S., Izumiya Y., Onoue Y., Tanaka T., Yamamoto M., Ishida T., Yamamura S., Kimura Y., Araki S., Arima Y., et al. Non-invasive testing for sarcopenia predicts future cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018;268:216–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.03.064. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lai S., Muscaritoli M., Andreozzi P., Sgreccia A., De Leo S., Mazzaferro S., Mitterhofer A.P., Pasquali M., Protopapa P., Spagnoli A., et al. Sarcopenia and cardiovascular risk indices in patients with chronic kidney disease on conservative and replacement therapy. Nutrition. 2019;62:108–114. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.12.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

