Carbon Dots as Promising Tools for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
- PMID: 33919096
- PMCID: PMC8122497
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13091991
Carbon Dots as Promising Tools for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
Abstract
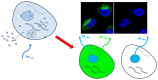
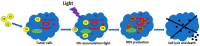
Carbon Dots (CDs) are the latest members of carbon-based nanomaterials, which since their discovery have attracted notable attention due to their chemical and mechanical properties, brilliant fluorescence, high photostability, and good biocompatibility. Together with the ease and affordable preparation costs, these intrinsic features make CDs the most promising nanomaterials for multiple applications in the biological field, such as bioimaging, biotherapy, and gene/drug delivery. This review will illustrate the most recent applications of CDs in the biomedical field, focusing on their biocompatibility, fluorescence, low cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, and theranostic properties to highlight above all their usefulness as a promising tool for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: bioimaging; cancer diagnosis cancer therapy; carbon dots; drug delivery; photodynamic therapy; photothermal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carbon dots: The next generation platform for biomedical applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Mar;96:887-903. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.060. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 30606603 Review.
-
Photonic Carbon Dots as an Emerging Nanoagent for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications.ACS Nano. 2020 Jun 23;14(6):6470-6497. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02114. Epub 2020 May 29. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32441509 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Biomedical Applications of Carbon Dots.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019 Jun 17;2(6):2317-2338. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b00112. Epub 2019 May 16. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019. PMID: 35030725
-
Regulating photochemical properties of carbon dots for theranostic applications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023 May-Jun;15(3):e1862. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1862. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36347269 Review.
-
Doped-carbon dots: Recent advances in their biosensing, bioimaging and therapy applications.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021 Jul;203:111743. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111743. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021. PMID: 33872828 Review.
Cited by
-
Orange-Peel-Derived Nanobiochar for Targeted Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 21;14(10):2249. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102249. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297682 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Dots: An Innovative Tool for Drug Delivery in Brain Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11783. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111783. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthetic natural carbon dots derived from Fuligo Plantae with inhibitory effect against alcoholic gastric ulcer.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jul 7;10:1223621. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1223621. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37484528 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Properties of Tricarboxylic Acid-Derived Carbon Dots.ACS Omega. 2022 Nov 22;7(48):44093-44102. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05503. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36506125 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Dots: Classification, Properties, Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications in Health Care-An Updated Review (2018-2021).Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 27;11(10):2525. doi: 10.3390/nano11102525. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34684966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altekruse S.F., Kosary C.L., Krapcho M., Neyman N., Aminou R., Waldron W. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2007. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2010.
-
- Block K.I., Gyllenhaal C., Lowe L., Amedei A., Amin A., Aquilano K., Arbiser J., Arreola A., Arzumanyan A., Ashraf S.S., et al. Designing a broad-spectrum integrative approach for cancer prevention and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S276–S304. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

