Nanovectorization of Prostate Cancer Treatment Strategies: A New Approach to Improved Outcomes
- PMID: 33919150
- PMCID: PMC8143094
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050591
Nanovectorization of Prostate Cancer Treatment Strategies: A New Approach to Improved Outcomes
Abstract
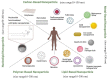
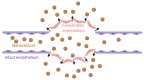
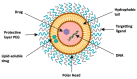
Prostate cancer (PC) is the most frequent male cancer in the Western world. Progression to Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) is a known consequence of androgen withdrawal therapy, making CRPC an end-stage disease. Combination of cytotoxic drugs and hormonal therapy/or genotherapy is a recognized modality for the treatment of advanced PC. However, this strategy is limited by poor bio-accessibility of the chemotherapy to tumor sites, resulting in an increased rate of collateral toxicity and incidence of multidrug resistance (MDR). Nanovectorization of these strategies has evolved to an effective approach to efficacious therapeutic outcomes. It offers the possibility to consolidate their antitumor activity through enhanced specific and less toxic active or passive targeting mechanisms, as well as enabling diagnostic imaging through theranostics. While studies on nanomedicine are common in other cancer types, only a few have focused on prostate cancer. This review provides an in-depth knowledge of the principles of nanotherapeutics and nanotheranostics, and how the application of this rapidly evolving technology can clinically impact CRPC treatment. With particular reference to respective nanovectors, we draw clinical and preclinical evidence, demonstrating the potentials and prospects of homing nanovectorization into CRPC treatment strategies.
Keywords: CRPC; Non-AR therapeutic targets; nanotheranostics; nanotherapies; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

