An Algorithm to Minimize Energy Consumption and Elapsed Time for IoT Workloads in a Hybrid Architecture
- PMID: 33919222
- PMCID: PMC8122349
- DOI: 10.3390/s21092914
An Algorithm to Minimize Energy Consumption and Elapsed Time for IoT Workloads in a Hybrid Architecture
Abstract
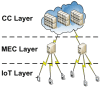
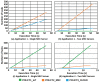
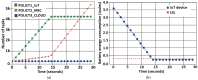
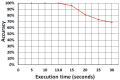
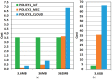
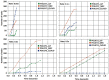
Advances in communication technologies have made the interaction of small devices, such as smartphones, wearables, and sensors, scattered on the Internet, bringing a whole new set of complex applications with ever greater task processing needs. These Internet of things (IoT) devices run on batteries with strict energy restrictions. They tend to offload task processing to remote servers, usually to cloud computing (CC) in datacenters geographically located away from the IoT device. In such a context, this work proposes a dynamic cost model to minimize energy consumption and task processing time for IoT scenarios in mobile edge computing environments. Our approach allows for a detailed cost model, with an algorithm called TEMS that considers energy, time consumed during processing, the cost of data transmission, and energy in idle devices. The task scheduling chooses among cloud or mobile edge computing (MEC) server or local IoT devices to achieve better execution time with lower cost. The simulated environment evaluation saved up to 51.6% energy consumption and improved task completion time up to 86.6%.
Keywords: Internet of things; cost minimization model; energy consumption; mobile edge computing; scheduling algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reinsel D., Gantz J., Rydning J. The Digitalization of The World: From Edge to Core. us44413318 ed. Volume 1. Seagate Inc.; Framingham, MA, USA: 2018. pp. 1–28. IDC White Paper.
-
- Chen T.Y.H., Ravindranath L., Deng S., Bahl P., Balakrishnan H. Glimpse: Continuous, Real-Time Object Recognition on Mobile Devices; Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, SenSys ’15; Seoul, Korea. 1–4 November 2015; New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2015. pp. 155–168. - DOI
-
- Matteussi K.J., Zanchetta B.F., Bertoncello G., Dos Santos J.D.D., dos Anjos J.C.S., Geyer C.F.R. Analysis and Performance Evaluation of Deep Learning on Big Data; Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC); Barcelona, Spain. 29 June–3 July 2019; pp. 1–6. - DOI
-
- Wang C., Dong C., Qin J., Yang X., Wen W. Energy-efficient Offloading Policy for Resource Allocation in Distributed Mobile Edge Computing; Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC); Natal, Brazil. 25–28 June 2018; pp. 00366–00372. - DOI
-
- Matteussi K.J., Geyer C.F.R., Xavier M.G., Rose C.A.F.D. Understanding and Minimizing Disk Contention Effects for Data-Intensive Processing in Virtualized Systems; Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on High Performance Computing Simulation (HPCS); Orleans, France. 16–20 July 2018; pp. 901–908. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

