β-Ionone Attenuates Dexamethasone-Induced Suppression of Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis in Human Dermal Fibroblasts
- PMID: 33919331
- PMCID: PMC8143342
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11050619
β-Ionone Attenuates Dexamethasone-Induced Suppression of Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis in Human Dermal Fibroblasts
Erratum in
-
Correction: Choi et al. β-Ionone Attenuates Dexamethasone-Induced Suppression of Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 619.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 21;14(10):1337. doi: 10.3390/biom14101337. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456274 Free PMC article.
Abstract
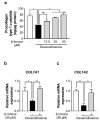
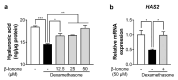
Stress is a major contributing factor of skin aging, which is clinically characterized by wrinkles, loss of elasticity, and dryness. In particular, glucocorticoids are generally considered key hormones for promoting stress-induced skin aging through binding to glucocorticoid receptors (GRs). In this work, we aimed to investigate whether β-ionone (a compound occurring in various foods such as carrots and almonds) attenuates dexamethasone-induced suppression of collagen and hyaluronic acid synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts, and to explore the mechanisms involved. We found that β-ionone promoted collagen production dose-dependently and increased mRNA expression levels, including collagen type I α 1 chain (COL1A1) and COL1A2 in dexamethasone-treated human dermal fibroblasts. It also raised hyaluronic acid synthase mRNA expression and hyaluronic acid levels. Notably, β-ionone inhibited cortisol binding to GR, subsequent dexamethasone-induced GR signaling, and the expression of several GR target genes. Our results reveal the strong potential of β-ionone for preventing stress-induced skin aging and suggest that its effects are related to the inhibition of GR signaling in human dermal fibroblasts.
Keywords: collagen; glucocorticoid; hyaluronic acid; stress; β-ionone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors would like to specify that the corresponding author, Taesun Park, holds several patents and is the CEO of a cosmetic company that commercializes products that contain similar ingredients to those that were investigated in the abovementioned article.
Figures





References
-
- Bukhari S.N.A., Roswandi N.L., Waqas M., Habib H., Hussain F., Khan S., Sohail M., Ramli N.A., Thu H.E., Hussain Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018;120:1682–1695. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.188. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cope G. Smoking and skin ageing: How aesthetic nurses can identify and prevent damage. J. Aesthetic Nurs. 2013;2:328–332. doi: 10.12968/joan.2013.2.7.328. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

