Bismuth-213 for Targeted Radionuclide Therapy: From Atom to Bedside
- PMID: 33919391
- PMCID: PMC8143329
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050599
Bismuth-213 for Targeted Radionuclide Therapy: From Atom to Bedside
Abstract
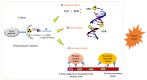
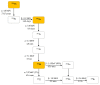
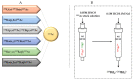
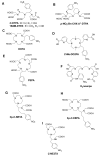
In contrast to external high energy photon or proton therapy, targeted radionuclide therapy (TRNT) is a systemic cancer treatment allowing targeted irradiation of a primary tumor and all its metastases, resulting in less collateral damage to normal tissues. The α-emitting radionuclide bismuth-213 (213Bi) has interesting properties and can be considered as a magic bullet for TRNT. The benefits and drawbacks of targeted alpha therapy with 213Bi are discussed in this review, covering the entire chain from radionuclide production to bedside. First, the radionuclide properties and production of 225Ac and its daughter 213Bi are discussed, followed by the fundamental chemical properties of bismuth. Next, an overview of available acyclic and macrocyclic bifunctional chelators for bismuth and general considerations for designing a 213Bi-radiopharmaceutical are provided. Finally, we provide an overview of preclinical and clinical studies involving 213Bi-radiopharmaceuticals, as well as the future perspectives of this promising cancer treatment option.
Keywords: bifunctional chelator; bismuth-213; radiopharmaceutical; targeted alpha therapy; targeted radionuclide therapy; vector molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bismuth-213 and actinium-225 -- generator performance and evolving therapeutic applications of two generator-derived alpha-emitting radioisotopes.Curr Radiopharm. 2012 Jul;5(3):221-7. doi: 10.2174/1874471011205030221. Curr Radiopharm. 2012. PMID: 22642390 Review.
-
Boosting Bismuth(III) Complexation for Targeted α-Therapy (TAT) Applications with the Mesocyclic Chelating Agent AAZTA.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Oct 24;61(43):e202207120. doi: 10.1002/anie.202207120. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 36073561 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted alpha therapy: part I.Curr Radiopharm. 2011 Jul;4(3):176. doi: 10.2174/1874471011104030176. Curr Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 22201706
-
Bismuth chelation for targeted alpha therapy: Current state of the art.Nucl Med Biol. 2022 Nov-Dec;114-115:168-188. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Nucl Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35753940 Review.
-
Evaluation of nitrogen-rich macrocyclic ligands for the chelation of therapeutic bismuth radioisotopes.Nucl Med Biol. 2015 May;42(5):428-438. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2014.12.007. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Nucl Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25684650
Cited by
-
A Radionuclide Generator of High-Purity Bi-213 for Instant Labeling.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 21;13(6):914. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060914. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34205580 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the sorption and desorption behavior of La3+ and Bi3+ by bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate modified activated carbon.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 1;14(47):34855-34867. doi: 10.1039/d4ra06276k. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39493547 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Radium Alpha Therapy in the Era of Nanomedicine: In Vivo Results.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):664. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010664. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calculation of alpha particle single-event spectra using a neural network.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 2;14:1394671. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1394671. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39416463 Free PMC article.
-
The application of radionuclide therapy for breast cancer.Front Nucl Med. 2024 Jan 10;3:1323514. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2023.1323514. eCollection 2023. Front Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39355029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dekempeneer Y., Keyaerts M., Krasniqi A., Puttemans J., Muyldermans S., Lahoutte T., D’huyvetter M., Devoogdt N. Targeted alpha therapy using short-lived alpha-particles and the promise of nanobodies as targeting vehicle. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016;16:1035–1047. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2016.1185412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dekempeneer Y., Caveliers V., Ooms M., Maertens D., Gysemans M., Lahoutte T., Xavier C., Lecocq Q., Maes K., Covens P., et al. The therapeutic efficacy of 213Bi-labeled sdAbs in a preclinical model of ovarian cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2020;17:3553–3566. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00580. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

