The Effects of Matriptase Inhibition on the Inflammatory and Redox Homeostasis of Chicken Hepatic Cell Culture Models
- PMID: 33919461
- PMCID: PMC8143509
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050450
The Effects of Matriptase Inhibition on the Inflammatory and Redox Homeostasis of Chicken Hepatic Cell Culture Models
Abstract
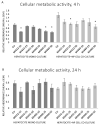
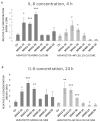
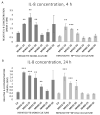
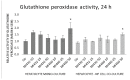
The function of the transmembrane serine protease matriptase is well described in mammals, but it has not been elucidated in avian species yet. Hence, the aim of the present study was to assess the effects of the 3-amidinophenylalanine (3-AphA)-type matriptase inhibitors MI432 and MI460 on the inflammatory and oxidative state of chicken primary hepatocyte mono-cultures and hepatocyte-nonparenchymal cell co-cultures, the latter serving as a proper model of hepatic inflammation in birds. Cell cultures were exposed to MI432 and MI460 for 4 and 24 h at 10, 25, and 50 µM concentrations, and thereafter the cellular metabolic activity, extracellular interleukin (IL-)6, IL-8, H2O2 and malondialdehyde concentrations were monitored. Both inhibitors caused a transient moderate reduction in the metabolic activity following 4 h exposure, which was restored after 24 h, reflecting the fast hepatic adaptation potential to matriptase inhibitor administration. Furthermore, MI432 triggered an intense elevation in the cellular proinflammatory IL-6 and IL-8 production after both incubation times in all concentrations, which was not coupled to enhanced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation based on unchanged H2O2 production, malondialdehyde levels and glutathione peroxidase activity. These data suggest that physiological matriptase activities might have a key function in retaining the metabolic and inflammatory homeostasis of the liver in chicken, without being a major modulator of the hepatocellular redox state.
Keywords: liver; oxidative stress; poultry; proinflammatory cytokines; serine proteases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Shi Y.E., Torri J., Yieh L., Wellstein A., Lippman M.E., Dickson R.B. Identification and characterization of a novel matrix-degrading protease from hormone-dependent human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1409–1415. - PubMed
-
- Hooper J.D., Campagnolo L., Goodarzi G., Truong T.N., Stuhlmann H., Quigley J.P. Mouse matriptase-2: Identification, characterization and comparative mRNA expression analysis with mouse hepsin in adult and embryonic tissues. Biochem. J. 2003;373:689–702. doi: 10.1042/bj20030390. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- List K., Haudenschild C.C., Szabo R., Chen W., Wahl S.M., Swaim W., Engelholm L.H., Behrendt N., Bugge T.H. Matriptase/MT-SP1 is required for postnatal survival, epidermal barrier function, hair follicle development, and thymic homeostasis. Oncogene. 2002;21:3765–3779. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205502. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

