Factors Differentiating the Antioxidant Activity of Macular Xanthophylls in the Human Eye Retina
- PMID: 33919673
- PMCID: PMC8070478
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10040601
Factors Differentiating the Antioxidant Activity of Macular Xanthophylls in the Human Eye Retina
Abstract
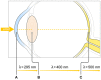
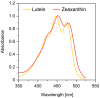
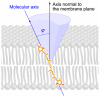
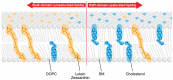
Macular xanthophylls, which are absorbed from the human diet, accumulate in high concentrations in the human retina, where they efficiently protect against oxidative stress that may lead to retinal damage. In addition, macular xanthophylls are uniquely spatially distributed in the retina. The zeaxanthin concentration (including the lutein metabolite meso-zeaxanthin) is ~9-fold greater than lutein concentration in the central fovea. These numbers do not correlate at all with the dietary intake of xanthophylls, for which there is a dietary zeaxanthin-to-lutein molar ratio of 1:12 to 1:5. The unique spatial distributions of macular xanthophylls-lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin-in the retina, which developed during evolution, maximize the protection of the retina provided by these xanthophylls. We will correlate the differences in the spatial distributions of macular xanthophylls with their different antioxidant activities in the retina. Can the major protective function of macular xanthophylls in the retina, namely antioxidant actions, explain their evolutionarily determined, unique spatial distributions? In this review, we will address this question.
Keywords: fovea; lipid bilayer; lutein; macular xanthophyll; zeaxanthin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Why is Zeaxanthin the Most Concentrated Xanthophyll in the Central Fovea?Nutrients. 2020 May 7;12(5):1333. doi: 10.3390/nu12051333. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32392888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Xanthophyll-Membrane Interactions Explain Their Selective Presence in the Retina and Brain?Foods. 2016 Mar;5(1):7. doi: 10.3390/foods5010007. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Foods. 2016. PMID: 27030822 Free PMC article.
-
Why has Nature Chosen Lutein and Zeaxanthin to Protect the Retina?J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Feb 21;5(1):326. doi: 10.4172/2155-9570.1000326. J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24883226 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of dietary zeaxanthin and lutein in macular health and function.Nutr Rev. 2023 May 10;81(6):670-683. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuac076. Nutr Rev. 2023. PMID: 36094616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macular zeaxanthins and lutein -- a review of dietary sources and bioavailability and some relationships with macular pigment optical density and age-related macular disease.Nutr Res Rev. 2007 Dec;20(2):163-79. doi: 10.1017/S0954422407842235. Nutr Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 19079868
Cited by
-
Light-Modulated Sunscreen Mechanism in the Retina of the Human Eye.J Phys Chem B. 2021 Jun 17;125(23):6090-6102. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c01198. Epub 2021 May 26. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 34038114 Free PMC article.
-
Raman Spectroscopy of Carotenoid Compounds for Clinical Applications-A Review.Molecules. 2022 Dec 17;27(24):9017. doi: 10.3390/molecules27249017. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Do Xanthophylls Protect Lipid Membranes from Oxidative Damage?J Phys Chem Lett. 2023 Aug 24;14(33):7440-7444. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c01374. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Phys Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37578906 Free PMC article.
-
Macular Pigment Carotenoids and Bisretinoid A2E.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1415:15-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-27681-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37440008 Review.
-
An Overview of Lutein in the Lipid Membrane.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12948. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612948. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629129 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schalch W., Bone R.A., Landrum J.T. The functional role of xantophylls in the primate retina. In: Landrum J.T., editor. Carotenoids Physical, Chemical, and Biological Functions and Properties. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2009. pp. 257–282.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

