Bioactive Components in Oat and Barley Grain as a Promising Breeding Trend for Functional Food Production
- PMID: 33919686
- PMCID: PMC8069901
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26082260
Bioactive Components in Oat and Barley Grain as a Promising Breeding Trend for Functional Food Production
Abstract
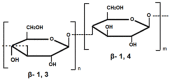
Cereal crops, such as oats and barley, possess a number of valuable properties that meet the requirements for functional diet components. This review summarized the available information about bioactive compounds of oat and barley grain. The results of studying the structure and physicochemical properties of the cell wall polysaccharides of barley and oat are presented. The main components of the flavonoids formation pathway are shown and data, concerning anthocyanins biosynthesis in various barley tissues, are discussed. Moreover, we analyzed the available information about structural and regulatory genes of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Hordeum vulgare L. genome, including β-glucan biosynthesis genes in Avena sativa L species. However, there is not enough knowledge about the genes responsible for biosynthesis of β-glucans and corresponding enzymes and plant polyphenols. The review also covers contemporary studies about collections of oat and barley genetic resources held by the N.I. Vavilov All-Russian Institute of Plant Genetic Resources (VIR). This review intended to provide information on the processes of biosynthesis of biologically active compounds in cereals that will promote further researches devoted to transcription factors controlling expression of structural genes and their role in other physiological processes in higher plants. Found achievements will allow breeders to create new highly productive varieties with the desirable properties.
Keywords: anthocyanins; antioxidants; biological role of pigments; flavonoids; gene families; polysaccharides; β-glucans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nikberg I.I. Functional products in the structure of modern nutrition. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2011;6:64–69. (In Russian)
-
- Functional Foods Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Ingredient (Carotenoids, Prebiotics & Probiotics, Fatty Acids, Dietary Fibers), by Product, by Application, and Segment Forecasts, 2019–2025. [(accessed on 28 January 2021)]; Available online: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/4764576/functional-foods-mark....
-
- Kornen N.N., Viktorova E.P., Evdokimova O.V. Methodological approaches to the creation of healthy food. Nutr. Issues. 2015;84:95–99. (In Russian) - PubMed
-
- Cheryl G.F., Sachin K.S., Arya S.S. Cereal based functional beverages: A review. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. Fernandesetal. 2018;8:914–919. doi: 10.15414/jmbfs.2018-19.8.3.914-919. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources