Perioperative ABO Blood Group Isoagglutinin Titer and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury after ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 33919744
- PMCID: PMC8070732
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10081679
Perioperative ABO Blood Group Isoagglutinin Titer and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury after ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
Abstract
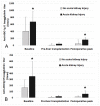
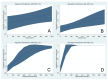
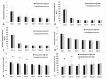
For ABO-incompatible liver transplantation (ABO-i LT), therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is performed preoperatively to reduce the isoagglutinin titer of anti-ABO blood type antibodies. We evaluated whether perioperative high isoagglutinin titer is associated with postoperative risk of acute kidney injury (AKI). In 130 cases of ABO-i LT, we collected immunoglobulin (Ig) G and Ig M isoagglutinin titers of baseline, pre-LT, and postoperative peak values. These values were compared between the patients with and without postoperative AKI. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association between perioperative isoagglutinin titers and postoperative AKI. Clinical and graft-related outcomes were compared between high and low baseline and postoperative peak isoagglutinin groups. The incidence of AKI was 42.3%. Preoperative baseline and postoperative peak isoagglutinin titers of both Ig M and Ig G were significantly higher in the patients with AKI than those without AKI. Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that preoperative baseline and postoperative peak Ig M isoagglutinin titers were significantly associated with the risk of AKI (baseline: odds ratio 1.06, 95% confidence interval 1.02 to 1.09; postoperative peak: odds ratio 1.08, 95% confidence interval 1.04 to 1.13). Cubic spline function curves show a positive relationship between the baseline and postoperative peak isoagglutinin titers and the risk of AKI. Clinical outcomes other than AKI were not significantly different according to the baseline and postoperative peak isoagglutinin titers. Preoperative high initial and postoperative peak Ig M isoagglutinin titers were significantly associated with the development of AKI. As the causal relationship between high isoagglutinin titers and risk of AKI is unclear, the high baseline and postoperative isoagglutinin titers could be used simply as a warning sign for the risk of AKI after liver transplantation.
Keywords: ABO blood-group system; acute kidney injury; anti-ABO blood type antibody; isoagglutinin; liver transplantation; living donor; therapeutic plasma exchange.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation is suitable in patients without ABO-matched donor.J Hepatol. 2013 Dec;59(6):1215-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.035. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23928408
-
ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation can be successfully conducted by monitoring IgM isoagglutinin titers during desensitization.Transfusion. 2020 Mar;60(3):598-606. doi: 10.1111/trf.15672. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Transfusion. 2020. PMID: 31957888
-
Significance of isoagglutinin titer in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation.J Clin Apher. 2014 Oct;29(5):243-50. doi: 10.1002/jca.21312. Epub 2013 Dec 24. J Clin Apher. 2014. PMID: 24375675
-
The critical role of therapeutic plasma exchange in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2022 Dec;21(6):538-542. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2022.06.019. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2022. PMID: 35831217 Review.
-
Isoagglutinin adsorption in ABO-incompatible transplantation.Transfus Apher Sci. 2010 Oct;43(2):231-5. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2010.07.016. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Transfus Apher Sci. 2010. PMID: 20667787 Review.
References
-
- Hilmi I.A., Damian D., Al-Khafaji A., Planinsic R., Boucek C., Sakai T., Chang C.-C.H., Kellum J.A. Acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: Incidence, risk factors, and effects on patient and graft outcomes. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015;114:919–926. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu556. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park M.H., Shim H.S., Kim W.H., Kim H.-J., Kim D.J., Lee S.-H., Kim C.S., Gwak M.S., Kim G.S. Clinical Risk Scoring Models for Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury after Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Retrospective Observational Study. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0136230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136230. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Utsumi M., Umeda Y., Sadamori H., Nagasaka T., Takaki A., Matsuda H., Shinoura S., Yoshida R., Nobuoka D., Satoh D., et al. Risk factors for acute renal injury in living donor liver transplantation: Evaluation of the RIFLE criteria. Transpl. Int. 2013;26:842–852. doi: 10.1111/tri.12138. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

