The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases
- PMID: 33919784
- PMCID: PMC8070705
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10040897
The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases
Abstract
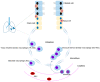
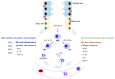
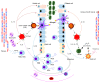
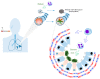
Macrophages play an important role in the innate and adaptive immune responses of organ systems, including the lungs, to particles and pathogens. Cumulative results show that macrophages contribute to the development and progression of acute or chronic inflammatory responses through the secretion of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines and the activation of transcription factors in the pathogenesis of inflammatory lung diseases, such as acute lung injury (ALI), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), ARDS related to COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)), allergic asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This review summarizes the functions of macrophages and their associated underlying mechanisms in the development of ALI, ARDS, COVID-19-related ARDS, allergic asthma, COPD, and IPF and briefly introduces the acute and chronic experimental animal models. Thus, this review suggests an effective therapeutic approach that focuses on the regulation of macrophage function in the context of inflammatory lung diseases.
Keywords: M1/M2 polarization; acute/chronic inflammatory diseases; cytokines; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez N.A., Quintana J.A., García-Silva S., Mazariegos M., De La Aleja A.G., Nicolás-Ávila J.A., Walter W., Adrover J.M., Crainiciuc G., Kuchroo V.K., et al. Phagocytosis imprints heterogeneity in tissue-resident macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2017;214:1281–1296. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161375. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Okuma T., Terasaki Y., Kaikita K., Kobayashi H., Kuziel W.A., Kawasuji M., Takeya M. C-C chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) deficiency improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by attenuation of both macrophage infiltration and production of macrophage-derived matrix metalloproteinases. J. Pathol. 2004;204:594–604. doi: 10.1002/path.1667. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

