Impact of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease Pandemic on Health-Related Quality of Life and Psychological Status: The Role of Physical Activity
- PMID: 33920147
- PMCID: PMC8069215
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18083992
Impact of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease Pandemic on Health-Related Quality of Life and Psychological Status: The Role of Physical Activity
Abstract
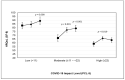
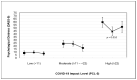
This study investigated the impact of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and psychological status among Saudi adults, and whether physical activity modifies this association. The participants were 518 adults aged ≥18 years (67.4% men). Using an online survey, data regarding demographic information, the impact of COVID-19 (assessed by the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5), HRQoL (Short Form-8), psychological distress (Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale), and physical activity behavior (International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form) were collected. The results demonstrate that adults reporting moderate or high levels of impact of COVID-19 had a lower HRQoL and higher psychological distress than adults reporting a low impact. HRQoL was higher for adults reporting any level impact (low, moderate, or high) of COVID-19 when they participated in recommended levels of physical activity (≥600 metabolic equivalent (MET)-min/week of total physical activity). Psychological distress was lower for adults reporting a high level of impact when they participated in recommended physical activity. Moderate or high levels of impact of COVID-19 were associated with a significantly lower HRQoL and higher psychological distress than the low impact of COVID-19. However, these associations were moderated by the recommended levels of physical activity.
Keywords: COVID-19; active; coronavirus; health; impact; pandemic; psychological stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Summary of Probable SARS Cases with Onset of Illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. [(accessed on 19 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table2004_04_21/en/
-
- Parnell D., Widdop P., Bond A., Wilson R. COVID-19, networks and sport. Manag. Sport Leis. 2020;1:1–7. doi: 10.1080/23750472.2020.1750100. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

