Hidden Targets in RAF Signalling Pathways to Block Oncogenic RAS Signalling
- PMID: 33920182
- PMCID: PMC8070103
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12040553
Hidden Targets in RAF Signalling Pathways to Block Oncogenic RAS Signalling
Abstract
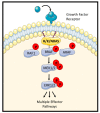
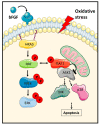
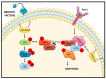
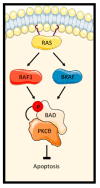
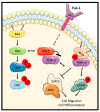
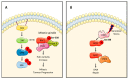
Oncogenic RAS (Rat sarcoma) mutations drive more than half of human cancers, and RAS inhibition is the holy grail of oncology. Thirty years of relentless efforts and harsh disappointments have taught us about the intricacies of oncogenic RAS signalling that allow us to now get a pharmacological grip on this elusive protein. The inhibition of effector pathways, such as the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway, has largely proven disappointing. Thus far, most of these efforts were aimed at blocking the activation of ERK. Here, we discuss RAF-dependent pathways that are regulated through RAF functions independent of catalytic activity and their potential role as targets to block oncogenic RAS signalling. We focus on the now well documented roles of RAF kinase-independent functions in apoptosis, cell cycle progression and cell migration.
Keywords: ASK; MST2; PLK; RAF kinase-independent; RAS; RHO-α; apoptosis; cancer therapy; cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

