Chronic Ouabain Prevents Na,K-ATPase Dysfunction and Targets AMPK and IL-6 in Disused Rat Soleus Muscle
- PMID: 33920198
- PMCID: PMC8069997
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22083920
Chronic Ouabain Prevents Na,K-ATPase Dysfunction and Targets AMPK and IL-6 in Disused Rat Soleus Muscle
Abstract
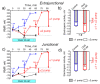
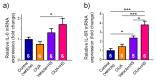
Sustained sarcolemma depolarization due to loss of the Na,K-ATPase function is characteristic for skeletal muscle motor dysfunction. Ouabain, a specific ligand of the Na,K-ATPase, has a circulating endogenous analogue. We hypothesized that the Na,K-ATPase targeted by the elevated level of circulating ouabain modulates skeletal muscle electrogenesis and prevents its disuse-induced disturbances. Isolated soleus muscles from rats intraperitoneally injected with ouabain alone or subsequently exposed to muscle disuse by 6-h hindlimb suspension (HS) were studied. Conventional electrophysiology, Western blotting, and confocal microscopy with cytochemistry were used. Acutely applied 10 nM ouabain hyperpolarized the membrane. However, a single injection of ouabain (1 µg/kg) prior HS was unable to prevent the HS-induced membrane depolarization. Chronic administration of ouabain for four days did not change the α1 and α2 Na,K-ATPase protein content, however it partially prevented the HS-induced loss of the Na,K-ATPase electrogenic activity and sarcolemma depolarization. These changes were associated with increased phosphorylation levels of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), its substrate acetyl-CoA carboxylase and p70 protein, accompanied with increased mRNA expression of interleikin-6 (IL-6) and IL-6 receptor. Considering the role of AMPK in regulation of the Na,K-ATPase, we suggest an IL-6/AMPK contribution to prevent the effects of chronic ouabain under skeletal muscle disuse.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Na,K-ATPase isozymes; hindlimb suspension; ouabain; resting membrane potential; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

