SARS-CoV-2 Serum Neutralization Assay: A Traditional Tool for a Brand-New Virus
- PMID: 33920222
- PMCID: PMC8069482
- DOI: 10.3390/v13040655
SARS-CoV-2 Serum Neutralization Assay: A Traditional Tool for a Brand-New Virus
Abstract
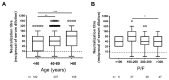
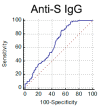
SARS-CoV-2 serum neutralization assay represents the gold standard for assessing antibody-mediated protection in naturally infected and vaccinated individuals. In the present study, 662 serum samples collected from February 2020 to January 2021 from acute and convalescent COVID-19 patients were tested to determine neutralizing antibody (NAb) titers using a microneutralization test (MNT) for live SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, IgA, and IgM directed against different viral antigens were measured by high-throughput automated platforms. We observed higher levels of NAbs in elderly (>60 years old) individuals and in patients presenting acute respiratory distress syndrome. SARS-CoV-2 NAbs develop as soon as five days from symptom onset and, despite a decline after the second month, persist for over 11 months, showing variable dynamics. Through correlation and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, we set up a testing algorithm, suitable for the laboratory workload, by establishing an optimal cutoff value of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG for convalescent plasma donors to exclude from MNT samples foreseen to have low/negative NAb titers and ineligible for plasma donation. Overall, MNT, although cumbersome and not suitable for routine testing of large sample sizes, remains the reference tool for the assessment of antibody-mediated immunity after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Smart testing algorithms may optimize the laboratory workflow to monitor antibody-mediated protection in COVID-19 patients, plasma donors, and vaccinated individuals.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; neutralizing antibodies; protective immunity; serology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barnes C.O., West A.P., Huey-Tubman K.E., Hoffmann M.A.G., Sharaf N.G., Hoffman P.R., Koranda N., Gristick H.B., Gaebler C., Muecksch F., et al. Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies. Cell. 2020;182:828–842.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The ARDS Definition Task Force Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. JAMA. 2012;307:2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- EVA. EVAg Portal. [(accessed on 8 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.european-virus-archive.com/virus/sars-cov-2-isolate-sars-cov....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

