Molecular Imaging of Apoptosis: The Case of Caspase-3 Radiotracers
- PMID: 33920463
- PMCID: PMC8069194
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22083948
Molecular Imaging of Apoptosis: The Case of Caspase-3 Radiotracers
Abstract
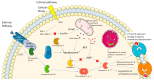
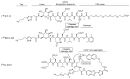
The molecular imaging of apoptosis remains an important method for the diagnosis and monitoring of the progression of certain diseases and the evaluation of the efficacy of anticancer apoptosis-inducing therapies. Among the multiple biomarkers involved in apoptosis, activated caspase-3 is an attractive target, as it is the most abundant of the executioner caspases. Nuclear imaging is a good candidate, as it combines a high depth of tissue penetration and high sensitivity, features necessary to detect small changes in levels of apoptosis. However, designing a caspase-3 radiotracer comes with challenges, such as selectivity, cell permeability and transient caspase-3 activation. In this review, we discuss the different caspase-3 radiotracers for the imaging of apoptosis together with the challenges of the translation of various apoptosis-imaging strategies in clinical trials.
Keywords: activity-based probe; caspase-3; positron emission tomography; radiotracer; single-photon emission computed tomography; substrate-based probe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

