Myopericarditis Associated with COVID-19 in a Pediatric Patient with Kidney Failure Receiving Hemodialysis
- PMID: 33920512
- PMCID: PMC8073656
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10040486
Myopericarditis Associated with COVID-19 in a Pediatric Patient with Kidney Failure Receiving Hemodialysis
Abstract
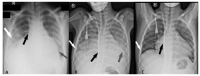
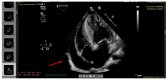
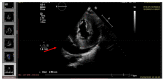
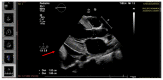
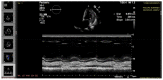
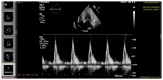
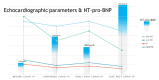
The outbreak of COVID-19 can be associated with cardiac and pulmonary involvement and is emerging as one of the most significant and life-threatening complications in patients with kidney failure receiving hemodialysis. Here, we report a critically ill case of a 13-year-old female patient with acute pericarditis and bilateral pleurisy, screened positive for SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR, presented with high fever, frequent dry cough, and dyspnea with tachypnea. COVID-19-induced myopericarditis has been noted to be a complication in patients with concomitant kidney failure with replacement therapy (KFRT). This article brings information in the light of our case experience, suggesting that the direct effect of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection on cardiac tissue was a significant contributor to myopericarditis in our patient. Further studies in this direction are required, as such associations have thus far been reported.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; children; end-stage kidney disease; hemodialysis; mortality; myopericarditis; pleurisy; post-infective complications; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac Involvement in a Patient With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 1;5(7):819-824. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1096. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32219357 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Myopericarditis in a Young Healthy Male.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2022 May 23;9(5):003361. doi: 10.12890/2022_003361. eCollection 2022. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35774730 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Myopericarditis in the Post COVID-19 Recovery Phase.Cureus. 2020 Oct 29;12(10):e11247. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11247. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33274129 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mannose-Binding Lectin and Inflammatory Markers in Establishing the Course and Prognosis of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children.Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;10(11):1744. doi: 10.3390/children10111744. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002835 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Infarction in Children after COVID-19 and Risk Factors for Thrombosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):884. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040884. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453932 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic Kidney Pathology in Children and Adolescents Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review.Children (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;9(10):1467. doi: 10.3390/children9101467. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- CDC Certain Medical Conditions and Risk for Severe COVID-19 Illness. [(accessed on 21 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

