Milk and Dairy Products: Good or Bad for Human Bone? Practical Dietary Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Osteoporosis
- PMID: 33920532
- PMCID: PMC8072827
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13041329
Milk and Dairy Products: Good or Bad for Human Bone? Practical Dietary Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Osteoporosis
Abstract
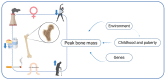
Osteoporosis affects women twice as often as men. Additionally, it is estimated that 0.3 million and 1.7 million people have hip fractures in the USA and Europe, respectively. Having a proper peak bone mass and keeping it as long as possible is especially important for osteoporosis prevention. One of the most important calcium sources is milk and dairy products. Breast milk is the best infant food, but milk should not be avoided later in life to prevent losing bone mass. On the other hand, more and more people limit their milk consumption and consume other dairy or non-dairy products. For example, they are usually replaced with plant beverages, which should be consumed carefully in several age groups. Additionally, an important element of milk and dairy products, as well as plant beverages, are probiotics and prebiotics, which may modulate bone turnover. Dietary recommendations focused on milk, and dairy products are an important element for the prevention of osteoporosis.
Keywords: bone health; bone mineral density; cow’s milk; cow’s milk allergy; lactose intolerance; nutrition; osteoporosis; plant milk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Janiszewska M., Kulik T., Dziedzic M., Żołnierczuk-Kieliszek D., Barańska A. Osteoporosis as a Social Problem- Pathogenesis, Symptoms and Risk Factors of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2015;96:106–114.
-
- Rosen C.J. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis. MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth, MA, USA: 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials