New Insights into Pathomechanisms and Treatment Possibilities for Lung Silicosis
- PMID: 33920534
- PMCID: PMC8072896
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22084162
New Insights into Pathomechanisms and Treatment Possibilities for Lung Silicosis
Abstract
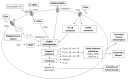
Inhalation of silica particles is an environmental and occupational cause of silicosis, a type of pneumoconiosis. Development of the lung silicosis is a unique process in which the vicious cycle of ingestion of inhaled silica particles by alveolar macrophages and their release triggers inflammation, generation of nodular lesions, and irreversible fibrosis. The pathophysiology of silicosis is complex, and interactions between the pathomechanisms have not been completely understood. However, elucidation of silica-induced inflammation cascades and inflammation-fibrosis relations has uncovered several novel possibilities of therapeutic targeting. This article reviews new information on the pathophysiology of silicosis and points out several promising treatment approaches targeting silicosis-related pathways.
Keywords: inflammation; lung fibrosis; oxidative stress; silica; silicosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conlict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Talini D., Paggiaro P.L., Falaschi F., Battolla L., Carrara M., Petrozzino M., Begliomini E., Bartolozzi C., Giuntini C. Chest radiography and high resolution computed tomography in the evaluation of workers exposed to silica dust: Relation with functional findings. Occup. Environ. Med. 1995;52:262–267. doi: 10.1136/oem.52.4.262. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

