Adrenoleukodystrophy Newborn Screening in California Since 2016: Programmatic Outcomes and Follow-Up
- PMID: 33920672
- PMCID: PMC8167547
- DOI: 10.3390/ijns7020022
Adrenoleukodystrophy Newborn Screening in California Since 2016: Programmatic Outcomes and Follow-Up
Abstract
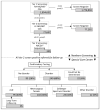
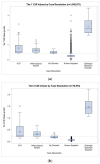
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a recent addition to the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel, prompting many states to begin screening newborns for the disorder. We provide California's experience with ALD newborn screening, highlighting the clinical and epidemiological outcomes observed as well as program implementation challenges. In this retrospective cohort study, we examine ALD newborn screening results and clinical outcomes for 1,854,631 newborns whose specimens were received by the California Genetic Disease Screening Program from 16 February 2016 through 15 February 2020. In the first four years of ALD newborn screening in California, 355 newborns screened positive for ALD, including 147 (41%) with an ABCD1 variant of uncertain significance (VUS) and 95 males diagnosed with ALD. After modifying cutoffs, we observed an ALD birth prevalence of 1 in 14,397 males. Long-term follow-up identified 14 males with signs of adrenal involvement. This study adds to a growing body of literature reporting on outcomes of newborn screening for ALD and offering a glimpse of what other large newborn screening programs can expect when adding ALD to their screening panel.
Keywords: adrenoleukodystrophy; evaluation; follow-up; newborn screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

