Behavior of Chemokine Receptor 6 (CXCR6) in Complex with CXCL16 Soluble form Chemokine by Molecular Dynamic Simulations: General Protein‒Ligand Interaction Model and 3D-QSAR Studies of Synthetic Antagonists
- PMID: 33920834
- PMCID: PMC8071165
- DOI: 10.3390/life11040346
Behavior of Chemokine Receptor 6 (CXCR6) in Complex with CXCL16 Soluble form Chemokine by Molecular Dynamic Simulations: General Protein‒Ligand Interaction Model and 3D-QSAR Studies of Synthetic Antagonists
Abstract
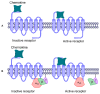
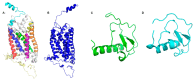
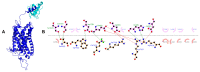
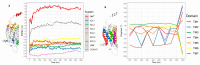
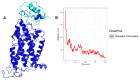
The CXCR6‒CXCL16 axis is involved in several pathological processes, and its overexpression has been detected in different types of cancer, such as prostate, breast, ovary, and lung cancer, along with schwannomas, in which it promotes invasion and metastasis. Moreover, this axis is involved in atherosclerosis, type 1 diabetes, primary immune thrombocytopenia, vitiligo, and other autoimmune diseases, in which it is responsible for the infiltration of different immune system cells. The 3D structure of CXCR6 and CXCL16 has not been experimentally resolved; therefore, homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations could be useful for the study of this signaling axis. In this work, a homology model of CXCR6 and a soluble form of CXCL16 (CXCR6‒CXCL16s) are reported to study the interactions between CXCR6 and CXCL16s through coarse-grained molecular dynamics (CG-MD) simulations. CG-MD simulations showed the two activation steps of CXCR6 through a decrease in the distance between the chemokine and the transmembrane region (TM) of CXCR6 and transmembrane rotational changes and polar interactions between transmembrane segments. The polar interactions between TM3, TM5, and TM6 are fundamental to functional conformation and the meta-active state of CXCR6. The interactions between D77-R280 and T243-TM7 could be related to the functional conformation of CXCR6; alternatively, the interaction between Q195-Q244 and N248 could be related to an inactive state due to the loss of this interaction, and an arginine cage broken in the presence of CXCL16s allows the meta-active state of CXCR6. A general protein‒ligand interaction supports the relevance of TM3‒TM5‒TM6 interactions, presenting three relevant pharmacophoric features: HAc (H-bond acceptor), HDn (H-bond donator), and Hph (hydrophobic), distributed around the space between extracellular loops (ECLs) and TMs. The HDn feature is close to TM3 and TM6; likewise, the HAc and Hph features are close to ECL1 and ECL2 and could block the rotation and interactions between TM3‒TM6 and the interactions of CXCL16s with the ECLs. Tridimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships (3D-QSAR) models show that the positive steric (VdW) and electrostatic fields coincide with the steric and positive electrostatic region of the exo-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane scaffold in the best pIC50 ligands. This substructure is close to the E274 residue and therefore relevant to the activity of CXCR6. These data could help with the design of new molecules that inhibit chemokine binding or antagonize the receptor based on the activation mechanism of CXCR6 and provoke a decrease in chemotaxis caused by the CXCR6‒CXCL16 axis.
Keywords: 3D-QSAR; CG-MD simulations; CXCL16s; CXCR6; docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
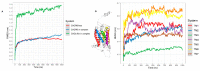



Similar articles
-
Site-directed mutagenesis of the chemokine receptor CXCR6 suggests a novel paradigm for interactions with the ligand CXCL16.Eur J Immunol. 2008 Aug;38(8):2337-50. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838269. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18629940
-
CXCR6/CXCL16 functions as a regulator in metastasis and progression of cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1806(1):42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20122997 Review.
-
The role of the CXCR6/CXCL16 axis in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May 10;132:112015. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112015. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38608478 Review.
-
CXCR6-CXCL16 Axis Promotes Breast Cancer by Inducing Oncogenic Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 16;13(14):3568. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143568. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298782 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine receptor CXCR6 and its ligand CXCL16 are expressed in carcinomas and inhibit proliferation.Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 15;68(12):4701-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0482. Cancer Res. 2008. Retraction in: Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 1;71(3):1196. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4378. PMID: 18559516 Retracted.
Cited by
-
Validation of the DLQI questionnaire in assessing the disease burden and principal aspects related to life quality of vitiligo patients.Front Psychol. 2024 May 30;15:1333723. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1333723. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38873521 Free PMC article.
-
The CXCL16/CXCR6 axis is linked to immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy.Genome Med. 2025 Jun 30;17(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13073-025-01498-6. Genome Med. 2025. PMID: 40588764 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Binding Epitope of an Anti-Mouse CCR6 Monoclonal Antibody (C6Mab-13) Using 1× Alanine Scanning.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;12(2):32. doi: 10.3390/antib12020032. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37218898 Free PMC article.
-
Ursolic acid interaction with transcription factors BRAF, V600E, and V600K: a computational approach towards new potential melanoma treatments.J Mol Model. 2024 Oct 10;30(11):373. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-06165-y. J Mol Model. 2024. PMID: 39387972
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

