Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 33920936
- PMCID: PMC8071291
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22084085
Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Huntington's Disease
Abstract
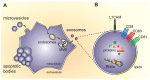
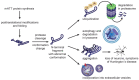
Huntington's disease (HD) is a rare hereditary autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder, which is caused by expression of mutant huntingtin protein (mHTT) with an abnormal number of glutamine repeats in its N terminus, and characterized by intracellular mHTT aggregates (inclusions) in the brain. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles that are secreted generally by all cell types and can be isolated from almost all body fluids such as blood, urine, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid. Exosomes may participate in the spreading of toxic misfolded proteins across the central nervous system in neurodegenerative diseases. In HD, such propagation of mHTT was observed both in vitro and in vivo. On the other hand, exosomes might carry molecules with neuroprotective effects. In addition, due to their capability to cross blood-brain barrier, exosomes hold great potential as sources of biomarkers available from periphery or carriers of therapeutics into the central nervous system. In this review, we discuss the emerging roles of exosomes in HD pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; biomarker; exosome; extracellular vesicle; huntingtin; neurodegeneration; polyQ; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yáñez-Mó M., Siljander P.R.-M., Andreu Z., Zavec A.B., Borràs F.E., Buzas E.I., Buzas K., Casal E., Cappello F., Carvalho J., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4:27066. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lakhal S., Wood M.J.A. Exosome nanotechnology: An emerging paradigm shift in drug delivery: Exploitation of exosome nanovesicles for systemic in vivo delivery of RNAi heralds new horizons for drug delivery across biological barriers. BioEssays. 2011;33:737–741. doi: 10.1002/bies.201100076. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

