Plant-Based Indole Alkaloids: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective
- PMID: 33921093
- PMCID: PMC8071433
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26082297
Plant-Based Indole Alkaloids: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective
Abstract
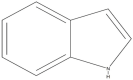
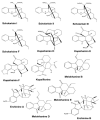
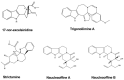
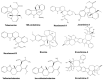
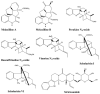
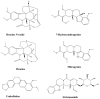
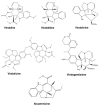
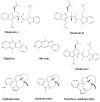
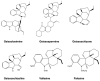
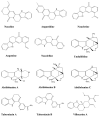
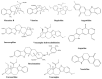
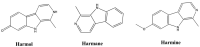
Plant-based indole alkaloids are very rich in pharmacological activities, and the indole nucleus is considered to contribute greatly to these activities. This review's fundamental objective is to summarize the pharmacological potential of indole alkaloids that have been derived from plants and provide a detailed evaluation of their established pharmacological activities, which may contribute to identifying new lead compounds. The study was performed by searching various scientific databases, including Springer, Elsevier, ACS Publications, Taylor and Francis, Thieme, Wiley Online Library, ProQuest, MDPI, and online scientific books. A total of 100 indole compounds were identified and reviewed. The most active compounds possessed a variety of pharmacological activities, including anticancer, antibacterial, antiviral, antimalarial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, analgesic, hypotensive, anticholinesterase, antiplatelet, antidiarrheal, spasmolytic, antileishmanial, lipid-lowering, antimycobacterial, and antidiabetic activities. Although some compounds have potent activity, some only have mild-to-moderate activity. The pharmacokinetic profiles of some of the identified compounds, such as brucine, mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, vindoline, and harmane, were also reviewed. Most of these compounds showed promising pharmacological activity. An in-depth pharmacological evaluation of these compounds should be performed to determine whether any of these indoles may serve as new leads.
Keywords: alkaloids; indole; pharmacokinetic profile; pharmacological activity; scientific databases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

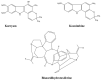
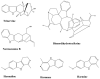
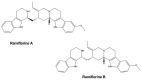

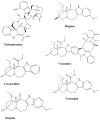
References
-
- Baeyer A. Ueber die Reduction aromatischer Verbindungen mittelst Zinkstaub. Justus Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1866;140:295–296. doi: 10.1002/jlac.18661400306. - DOI
-
- Dewick P.M. Essentials of Organic Chemistry: For Students of Pharmacy, Medicinal Chemistry and Biological Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

