Role of Thrombin in Central Nervous System Injury and Disease
- PMID: 33921354
- PMCID: PMC8070021
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11040562
Role of Thrombin in Central Nervous System Injury and Disease
Abstract
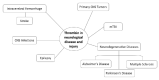
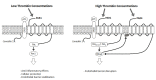
Thrombin is a Na+-activated allosteric serine protease of the chymotrypsin family involved in coagulation, inflammation, cell protection, and apoptosis. Increasingly, the role of thrombin in the brain has been explored. Low concentrations of thrombin are neuroprotective, while high concentrations exert pathological effects. However, greater attention regarding the involvement of thrombin in normal and pathological processes in the central nervous system is warranted. In this review, we explore the mechanisms of thrombin action, localization, and functions in the central nervous system and describe the involvement of thrombin in stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage, neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, and primary central nervous system tumors. We aim to comprehensively characterize the role of thrombin in neurological disease and injury.
Keywords: TBI; blood–brain barrier; glioblastoma; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation; protease-activated receptor; prothrombin; thrombin.
Conflict of interest statement
No disclosures.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

