Effects of Home Confinement on the Intensity of Physical Activity during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Team Handball According to Country, Gender, Competition Level, and Playing Position: A Worldwide Study
- PMID: 33921377
- PMCID: PMC8069346
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18084050
Effects of Home Confinement on the Intensity of Physical Activity during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Team Handball According to Country, Gender, Competition Level, and Playing Position: A Worldwide Study
Abstract
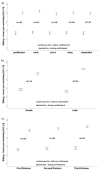
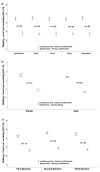
This study investigated effects of home confinement on physical activity (PA) in Team Handball during the COVID-19 outbreak. A total of 1359 handball players participated (age: 23 ± 6 years). Participants from Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa answered an online version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) considering "before" and "during" confinement. COVID-19 home confinement has had a negative effect on PA (vigorous, moderate, walking, and overall). The largest decrease was in the sum parameter "all PA" (MET (metabolic equivalent of task)-min/week, ηp2 = 0.903; min/week, ηp2 = 0.861). Daily sitting time increased from 2.7 to 5.0 h per weekday (p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.669). For gender, continent, country, level of handball league, and playing position, no significant differences (group and interaction effects) were observed. The largest change in PA behavior was in walking (minutes per day: ηp2 = 0.755), with males displaying the greatest decrease (from 62 ± 11 to 30 ± 14 min per weekday; d = 2.67). In terms of magnitude, difference between genders was greatest for sitting time (difference in d = 1.20). In conclusion, while COVID-19 measures were essential to preserve public health, PA was compromised and sedentary behavior increased because of these public health measures regardless of gender, playing position, and competition level.
Keywords: COVID-19; home confinement; lockdown; physical activity; stress; team handball.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ammar A., Brach M., Trabelsi K., Chtourou H., Boukhris O., Masmoudi L., Bouaziz B., Bentlage E., How D., Ahmed M., et al. Effects of COVID-19 home confinement on eating behaviour and physical activity: Results of the ECLB-COVID19 International Online Survey. Nutrients. 2020;12:1583. doi: 10.3390/nu12061583. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous