The Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Serum Creatinine in Patients Undergoing Partial Nephrectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33921503
- PMCID: PMC8069991
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10081636
The Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Serum Creatinine in Patients Undergoing Partial Nephrectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
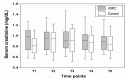
Renal function declines after partial nephrectomy due to ischemic reperfusion injury induced by surgical insult or renal artery clamping. The effect of remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) on reducing renal injury after partial nephrectomy has not been studied regarding urinary biomarkers. Eighty-one patients undergoing partial nephrectomy were randomly assigned to either RIPC or the control group. RIPC protocol consisted of four cycles of five-min inflation and deflation of a blood pressure cuff to 250 mmHg. Serum creatinine levels were compared at the following time points: preoperative baseline, immediate postoperative, on the first and third days after surgery, and two weeks after surgery. The incidence of acute kidney injury, other surgical complication rates, and urinary biomarkers, including urine creatinine, β-2 microglobulin, microalbumin, and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase were compared. Split renal functions measured by renal scan were compared up to 18 months after surgery. There was no significant difference in the serum creatinine level on the first postoperative day (median (interquartile range) 0.87 mg/dL (0.72-1.03) in the RIPC group vs. 0.92 mg/dL (0.71-1.12) in the control group, p = 0.728), nor at any other time point. There was no significant difference in the incidence of acute kidney injury. Secondary outcomes, including urinary biomarkers, were not significantly different between the groups. RIPC showed no significant effect on the postoperative serum creatinine level of the first postoperative day. We could not reveal any significant difference in the urinary biomarkers and clinical outcomes. However, further larger randomized trials are required, because our study was not sufficiently powered for the secondary outcomes.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; partial nephrectomy; remote ischemic preconditioning; urinary biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on serum creatinine in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Sep 4;19(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2820-3. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30180887 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on renal protection in patients undergoing laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: a 'blinded' randomised controlled trial.BJU Int. 2013 Jul;112(1):74-80. doi: 10.1111/bju.12004. Epub 2013 Mar 4. BJU Int. 2013. PMID: 23452148 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on kidney injury among high-risk patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a randomized clinical trial.JAMA. 2015 Jun 2;313(21):2133-41. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.4189. JAMA. 2015. PMID: 26024502 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning for prevention of acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Oct;64(4):574-83. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.04.029. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24954246
-
Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on postoperative acute kidney injury among patients undergoing cardiac and vascular interventions: a meta-analysis.J Nephrol. 2017 Feb;30(1):19-33. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0301-x. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27091767 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Multimodal Bundle with Remote Ischemic Preconditioning and Intrathecal Analgesia on Early Recovery of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;14(8):1985. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081985. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454891 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Short-Term Restriction of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acid Intake for Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind, Translational Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Sep 6;11(17):e025229. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.025229. Epub 2022 Sep 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36056721 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of remote ischaemic preconditioning on outcomes following non-cardiac non-vascular surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Perioper Med (Lond). 2023 Apr 10;12(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13741-023-00297-0. Perioper Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37038219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costunolide prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by reducing autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation, and DNA damage.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(10):1168-1176. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.71779.15596. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37736519 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of remote ischemic conditioning in renal transplantation and partial nephrectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Surg. 2023 Apr 5;10:1024650. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1024650. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37091267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chawla L.S., Bellomo R., Bihorac A., Goldstein S.L., Siew E.D., Bagshaw S.M., Bittleman D., Cruz D., Endre Z., Fitzgerald R.L., et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017;13:241–257. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou H., Yang L., Wang G., Zhang C., Fang Z., Lei G., Shi S., Li J. Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Prevents Postoperative Acute Kidney Injury After Open Total Aortic Arch Replacement: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2019;129:287–293. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004127. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

