Protective Role of a TMPRSS2 Variant on Severe COVID-19 Outcome in Young Males and Elderly Women
- PMID: 33921689
- PMCID: PMC8073081
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12040596
Protective Role of a TMPRSS2 Variant on Severe COVID-19 Outcome in Young Males and Elderly Women
Abstract
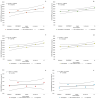
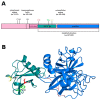
The protease encoded by the TMPRSS2 gene facilitates viral infections and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2. We analyzed the TMPRSS2 sequence and correlated the protein variants with the clinical features of a cohort of 1177 patients affected by COVID-19 in Italy. Nine relatively common variants (allele frequency > 0.01) and six missense variants which may affect the protease activity according to PolyPhen-2 in HumVar-trained mode were identified. Among them, p.V197M (p.Val197Met) (rs12329760) emerges as a common variant that has a deleterious effect on the protease and a protective effect on the patients. Its role appears particularly relevant in two subgroups of patients-young males and elderly women-and among those affected by co-morbidities, where the variant frequency is higher among individuals who were mildly affected by the disease and did not need hospitalization or oxygen therapy than among those more severely affected, who required oxygen therapy, ventilation or intubation. This study provides useful information for the identification of patients at risk of developing a severe form of COVID-19, and encourages the usage of drugs affecting the expression of TMPRSS2 or inhibiting protein activity.
Keywords: COVID-19; TMPRSS2; V197M; Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES); missense mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lucas J.M., Heinlein C., Kim T., Hernandez S.A., Malik M.S., True L.D., Morrissey C., Corey E., Montgomery B., Mostaghel E., et al. The Androgen-Regulated Protease TMPRSS2 Activates a Proteolytic Cascade Involving Components of the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:1310–1325. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ko C.J., Huang C.C., Lin H.Y., Juan C.P., Lan S.W., Shyu H.Y., Wu S.R., Hsiao P.W., Huang H.P., Shun C.T., et al. Androgen-Induced TMPRSS2 Activates Matriptase and Promotes Extracellular Matrix Degradation, Prostate Cancer Cell Invasion, Tumor Growth, and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2015;75:2949–2960. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3297. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heurich A., Hofmann-Winkler H., Gierer S., Liepold T., Jahn O., Pohlmann S. TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 Cleave ACE2 Differentially and Only Proteolysis by TMPRSS2 Augments Entry Driven by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Virol. 2014;88:1293–1307. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02202-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertram S., Dijkman R., Habjan M., Heurich A., Gierer S., Glowacka I., Welsch K., Winkler M., Schneider H., Hofmann-Winkler H., et al. TMPRSS2 Activates the Human Coronavirus 229E for Cathepsin-Independent Host Cell Entry and Is Expressed in Viral Target Cells in the Respiratory Epithelium. J. Virol. 2013;87:6150–6160. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03372-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

