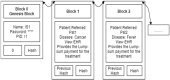
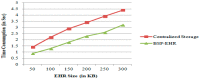
BSF-EHR: Blockchain Security Framework for Electronic Health Records of Patients
- PMID: 33921738
- PMCID: PMC8073400
- DOI: 10.3390/s21082865
BSF-EHR: Blockchain Security Framework for Electronic Health Records of Patients
Abstract
In the current epoch of smart homes and cities, personal data such as patients' names, diseases and addresses are often violated. This is frequently associated with the safety of the electronic health records (EHRs) of patients. EHRs have numerous benefits worldwide, but at present, EHR information is subject to considerable security and privacy issues. This paper proposes a way to provide a secure solution to these issues. Previous sophisticated techniques dealing with the protection of EHRs usually make data inaccessible to patients. These techniques struggle to balance data confidentiality, patient demand and constant interaction with provider data. Blockchain technology solves the above problems since it distributes information in a transactional and decentralized manner. The usage of blockchain technology could help the health sector to balance the accessibility and privacy of EHRs. This paper proposes a blockchain security framework (BSF) to effectively and securely store and keep EHRs. It presents a safe and proficient means of acquiring medical information for doctors, patients and insurance agents while protecting the patient's data. This work aims to examine how our proposed framework meets the security needs of doctors, patients and third parties and how the structure addresses safety and confidentiality concerns in the healthcare sector. Simulation outcomes show that this framework efficiently protects EHR data.
Keywords: EHR; blockchain; confidentiality and storage; security.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design of Secure Protocol for Cloud-Assisted Electronic Health Record System Using Blockchain.Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 21;20(10):2913. doi: 10.3390/s20102913. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32455635 Free PMC article.
-
A Controllable Secure Blockchain-Based Electronic Healthcare Records Sharing Scheme.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 4;2022:2058497. doi: 10.1155/2022/2058497. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35281527 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare 5.0: A secure and distributed network for system informatics in medical surgery.Int J Med Inform. 2024 Jun;186:105415. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2024.105415. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Int J Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 38520907
-
A Blockchain Framework for Patient-Centered Health Records and Exchange (HealthChain): Evaluation and Proof-of-Concept Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Aug 31;21(8):e13592. doi: 10.2196/13592. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31471959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health Records Database and Inherent Security Concerns: A Review of the Literature.Cureus. 2022 Oct 11;14(10):e30168. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30168. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36397924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of privacy protection technology to healthcare big data.Digit Health. 2024 Nov 4;10:20552076241282242. doi: 10.1177/20552076241282242. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39502481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun Y., Zhang D. Diagnosis and Analysis of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Electronic Health Records. IEEE Access. 2019;7:86115–86120. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918625. - DOI
-
- Shahnaz A., Qamar U., Khalid A. Using blockchain for electronic health records. IEEE Access. 2019;7:147782–147795. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946373. - DOI
-
- Grewal M.K., Sood K. Blockchain: A Disruptive Technology. J. Open Source Dev. 2020;7:1–4.
-
- McGhin T., Choo K.K., Liu C.Z., He D. Blockchain in healthcare applications: Research challenges and opportunities. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019;135:62–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2019.02.027. - DOI
-
- Wagh S.B., Murthy J.K. Securing Health Care Data for Medical Research Using Blockchain Technology. J. Adv. Electron. Des. 2018;1:17–23.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources