Blastocystis sp. Carriage and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Is the Association Already Established?
- PMID: 33921803
- PMCID: PMC8072823
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10040340
Blastocystis sp. Carriage and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Is the Association Already Established?
Abstract
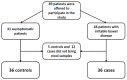
Background: The aim of the present study is to describe the occurrence of Blastocystis sp. detection among asymptomatic subjects and patients with irritable bowel syndrome in order to evaluate the potential association between irritable bowel syndrome and the parasitic infection.
Methods: Cross-sectional study where adult patients with irritable bowel syndrome diagnosed according to Rome IV criteria were included. A control group was formed by asymptomatic subjects older than 18 years. Exclusion criteria were: immunosuppressive condition or having received any drug with demonstrated activity against Blastocystis sp. within the last 6 months before study inclusion. Epidemiological and clinical information was collected from all included participants. Two stool samples were obtained from all participants: one sample for microscopic examination and one sample for Blastocystis sp. PCR detection. Blastocystis sp. infection was defined by the positivity of any of the diagnostic techniques.
Results: Seventy-two participants were included (36 asymptomatic subjects and 36 patients with irritable bowel syndrome). Thirty-five (48.6%) were men, and median age of participants was 34 (IQR 29-49) years. The overall rate of Blastocystis sp. carriage was 27.8% (20/72). The prevalence assessed through microscopic examination was 22.2% (16/72), while the prevalence measured by PCR was 15.3% (11/72). When comparing the presence of Blastocystis sp. between asymptomatic subjects and IBS patients, we did not find any statistically significant difference (36.1% vs. 19.4% respectively, p = 0.114).
Conclusions: regarding the occurrence of Blastocystis sp., no differences were found between asymptomatic participants and patients with irritable bowel disease irrespective of the diagnostic technique performed.
Keywords: Blastocystis sp.; irritable bowel syndrome; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Similar articles
-
Blastocystis subtypes isolated from irritable bowel syndrome patients and co-infection with Helicobacter pylori.Parasitol Res. 2018 Jan;117(1):127-137. doi: 10.1007/s00436-017-5679-4. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 29138961
-
Molecular characterization of Blastocystis hominis in irritable bowel syndrome patients and nursing staff in public and private clinic in Iraq.Ann Parasitol. 2022;68(4):715-720. doi: 10.17420/ap6804.478. Ann Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 37702208
-
The prevalence of intestinal parasites is not greater among individuals with irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based case-control study.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;13(3):507-513.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.07.065. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25229421
-
The neglected role of Blastocystis sp. and Giardia lamblia in development of irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2022 Jan;162:105215. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105215. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 34592369
-
Blastocystis subtypes and their association with Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Med Hypotheses. 2018 Jul;116:4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Med Hypotheses. 2018. PMID: 29857906 Review.
Cited by
-
Blastocystis colonization and associations with population parameters in Thai adults.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jul 9;18(7):e0012292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012292. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38980911 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Blastocystis spp. in the Etiology of Gastrointestinal and Autoimmune Diseases.Pathogens. 2025 Mar 25;14(4):313. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14040313. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40333047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtype Distribution of Blastocystis spp. in Patients with Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Northern Spain.Microorganisms. 2024 May 27;12(6):1084. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061084. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930466 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota Shifting in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Mysterious Role of Blastocystis sp.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 20;9:890127. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.890127. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35795640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blastocystis hominis; Friend or Foe.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2024 Nov;23(5):28-33. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2024. PMID: 39534663 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources