An Improved Sensing Method of a Robotic Ultrasound System for Real-Time Force and Angle Calibration
- PMID: 33922012
- PMCID: PMC8122492
- DOI: 10.3390/s21092927
An Improved Sensing Method of a Robotic Ultrasound System for Real-Time Force and Angle Calibration
Abstract
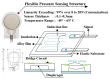
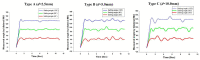
An ultrasonic examination is a clinically universal and safe examination method, and with the development of telemedicine and precision medicine, the robotic ultrasound system (RUS) integrated with a robotic arm and ultrasound imaging system receives increasing attention. As the RUS requires precision and reproducibility, it is important to monitor the real-time calibration of the RUS during examination, especially the angle of the probe for image detection and its force on the surface. Additionally, to speed up the integration of the RUS and the current medical ultrasound system (US), the current RUSs mostly use a self-designed fixture to connect the probe to the arm. If the fixture has inconsistencies, it may cause an operating error. In order to improve its resilience, this study proposed an improved sensing method for real-time force and angle calibration. Based on multichannel pressure sensors, an inertial measurement unit (IMU), and a novel sensing structure, the ultrasonic probe and robotic arm could be simply and rapidly combined, which rendered real-time force and angle calibration at a low cost. The experimental results show that the average success rate of the downforce position identification achieved was 88.2%. The phantom experiment indicated that the method could assist the RUS in the real-time calibration of both force and angle during an examination.
Keywords: inertial measurement unit (IMU); low cost; multichannel pressure sensors; phantom test; robotic ultrasound system (RUS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided needle insertion robotic system for percutaneous puncture.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Mar;16(3):475-484. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02300-1. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33484429
-
Automatic ultrasound scanning robotic system with optical waveguide-based force measurement.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Jun;16(6):1015-1025. doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02385-2. Epub 2021 May 3. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33939078
-
Force-guided autonomous robotic ultrasound scanning control method for soft uncertain environment.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Dec;16(12):2189-2199. doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02462-6. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 34373973
-
Robotic ultrasound imaging: State-of-the-art and future perspectives.Med Image Anal. 2023 Oct;89:102878. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102878. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Med Image Anal. 2023. PMID: 37541100 Review.
-
A review of calibration techniques for freehand 3-D ultrasound systems.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005 Feb;31(2):143-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2004.11.001. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005. Corrected and republished in: Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005 Apr;31(4):449-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2004.11.015. PMID: 15708453 Corrected and republished. Review.
Cited by
-
Autonomous robotic ultrasound scanning system: a key to enhancing image analysis reproducibility and observer consistency in ultrasound imaging.Front Robot AI. 2025 Feb 5;12:1527686. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2025.1527686. eCollection 2025. Front Robot AI. 2025. PMID: 39975565 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Ultrasound Robot with Force/torque Measurement and Control for Safe and Efficient Scanning.IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2023;72:1-12. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3239925. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2023. PMID: 37323850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakadate R., Solis J., Takanishi A., Sugawara M., Niki K., Minagawa E. ROMANSY 18 Robot Design, Dynamics and Control. Springer; Vienna, Austria: 2010. Development of the ultrasound probe holding robot WTA-1RII and an automated scanning algorithm based on ultrasound image feedback; pp. 359–366.
-
- Samei G., Tsang K., Kesch C., Lobo J., Hor S., Mohareri O., Chang S., Goldenberg L., Black P.C., Salcudean S. A partial augmented reality system with live ultrasound and registered preoperative MRI for guiding robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Med. Image Anal. 2020;60:101588. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101588. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

