Overcoming the Challenges of High Quality RNA Extraction from Core Needle Biopsy
- PMID: 33922016
- PMCID: PMC8143498
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11050621
Overcoming the Challenges of High Quality RNA Extraction from Core Needle Biopsy
Abstract
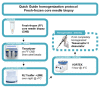
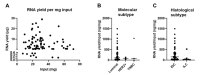
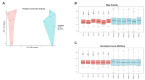
The use of gene expression profiling (GEP) in cancer management is rising, as GEP can be used for disease classification and diagnosis, tailoring treatment to underlying genetic determinants of pharmacological response, monitoring of therapy response, and prognosis. However, the reliability of GEP heavily depends on the input of RNA in sufficient quantity and quality. This highlights the need for standard procedures to ensure best practices for RNA extraction from often small tumor biopsies with variable tissue handling. We optimized an RNA extraction protocol from fresh-frozen (FF) core needle biopsies (CNB) from breast cancer patients and from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue when FF CNB did not yield sufficient RNA. Methods to avoid ribonucleases andto homogenize or to deparaffinize tissues and the impact of tissue composition on RNA extraction were studied. Additionally, RNA's compatibility with the nanoString nCounter® technology was studied. This technology platform enables GEP using small RNA fragments. After optimization of the protocol, RNA of high quality and sufficient quantity was obtained from FF CNB in 92% of samples. For the remaining 8% of cases, FFPE material prepared by the pathology department was used for RNA extraction. Both resulting RNA end products are compatible with the nanoString nCounter® technology.
Keywords: RNA; biopsy; breast cancer; formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; fresh-frozen; gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Cucchi D.G., Bachas C., Heuvel-Eibrink M.M.V.D., Arentsen-Peters S.T., Kwidama Z.J., Schuurhuis G.J., Assaraf Y.G., De Haas V., Kaspers G.J., Cloos J. Harnessing Gene Expression Profiles for the Identification of Ex Vivo Drug Response Genes in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers. 2020;12:1247. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Song J., Gao Z., Huo X., Zhang Y., Wang W., Qi J., Zheng S. Analysis of gene expression profiles of non-small cell lung cancer at different stages reveals significantly altered biological functions and candidate genes. Oncol. Rep. 2017;37:1736–1746. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5380. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Apostolou P., Iliopoulos A.C., Parsonidis P., Papasotiriou I. Gene expression profiling as a potential predictor between normal and cancer samples in gastrointestinal carcinoma. [(accessed on 30 November 2020)];Oncotarget. 2019 10:3328–3338. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26913. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31164955. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

