Updated Mechanisms of GCN5-The Monkey King of the Plant Kingdom in Plant Development and Resistance to Abiotic Stresses
- PMID: 33922251
- PMCID: PMC8146787
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10050979
Updated Mechanisms of GCN5-The Monkey King of the Plant Kingdom in Plant Development and Resistance to Abiotic Stresses
Abstract
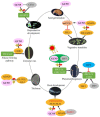
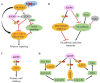
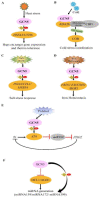
Histone modifications are the main epigenetic mechanisms that regulate gene expression, chromatin structure, and plant development, among which histone acetylation is one of the most important and studied epigenetic modifications. Histone acetylation is believed to enhance DNA access and promote transcription. GENERAL CONTROL NON-REPRESSIBLE 5 (GCN5), a well-known enzymatic protein responsible for the lysine acetylation of histone H3 and H4, is a universal and crucial histone acetyltransferase involved in gene transcription and plant development. Many studies have found that GCN5 plays important roles in the different development stages of Arabidopsis. In terms of exogenous stress conditions, GCN5 is also involved in the responses to heat stress, cold stress, and nutrient element deficiency by regulating the related gene expression to maintain the homeostasis of some key metabolites (e.g., cellulose) or ions (e.g., phosphate, iron); in addition, GCN5 is involved in the phytohormone pathways such as ethylene, auxin, and salicylic acid to play various roles during the plant lifecycle. Some of the pathways involved by GCN5 also interwind to regulate specific physiological processes or developmental stages. Here, interactions between various developmental events and stress-resistant pathways mediated by GCN5 are comprehensively addressed and the underlying mechanisms are discussed in the plant. Studies with some interacting factors such as ADA2b provided valuable information for the complicated histone acetylation mechanisms. We also suggest the future focuses for GCN5 functions and mechanisms such as functions in seed development/germination stages, exploration of novel interaction factors, identification of more protein substrates, and application of advanced biotechnology-CRISPR in crop genetic improvement, which would be helpful for the complete illumination of roles and mechanisms of GCN5.
Keywords: ADA2b; GCN5; abiotic stress; histone modification; organ development; signaling pathways; trichome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GCN5 modulates salicylic acid homeostasis by regulating H3K14ac levels at the 5' and 3' ends of its target genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):5953-5966. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa369. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32396165 Free PMC article.
-
Histone dynamics and roles of histone acetyltransferases during cold-induced gene regulation in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2010 Sep;74(1-2):183-200. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9665-9. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Plant Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20661629
-
Gibberellin Signaling through RGA Suppresses GCN5 Effects on Arabidopsis Developmental Stages.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 19;25(12):6757. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126757. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928464 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in understanding the roles of plant HAT and HDAC in non-histone protein acetylation and deacetylation.Planta. 2024 Sep 12;260(4):93. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04518-8. Planta. 2024. PMID: 39264431 Review.
-
The roles of histone acetylation in seed performance and plant development.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Nov;84:125-133. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25270163 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and gene duplication of the epigenetic regulators in Fagaceae.Physiol Plant. 2022 Sep;174(5):e13788. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13788. Physiol Plant. 2022. PMID: 36169620 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling VIGS with Short- and Long-Term Stress Exposure to Understand the Fiskeby III Iron Deficiency Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):647. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010647. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614091 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetyltransferase TaHAG1 interacts with TaPLATZ5 to activate TaPAD4 expression and positively contributes to powdery mildew resistance in wheat.New Phytol. 2022 Oct;236(2):590-607. doi: 10.1111/nph.18372. Epub 2022 Jul 28. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35832009 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor CAMTA2 interacts with the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and regulates grain weight in wheat.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 25;36(12):4895-913. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae261. Online ahead of print. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 39321218 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study between Exogenously Applied Plant Growth Hormones versus Metabolites of Microbial Endophytes as Plant Growth-Promoting for Phaseolus vulgaris L.Cells. 2021 Apr 29;10(5):1059. doi: 10.3390/cells10051059. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33946942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costelloe T., Lowndes N.F. Chromatin assembly and signalling the end of DNA repair requires acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56. Subcell Biochem. 2010;50:43–54. - PubMed
-
- Pandey R., Muller A., Napoli C.A., Selinger D.A., Pikaard C.S., Richards E.J., Bender J., Mount D.W., Jorgensen R.A. Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:5036–5055. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf660. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

