Biogenic Synthesis of NiO Nanoparticles Using Areca catechu Leaf Extract and Their Antidiabetic and Cytotoxic Effects
- PMID: 33922292
- PMCID: PMC8122846
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092448
Biogenic Synthesis of NiO Nanoparticles Using Areca catechu Leaf Extract and Their Antidiabetic and Cytotoxic Effects
Abstract
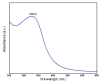
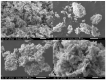
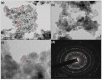
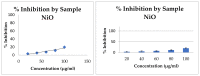
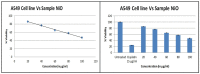
Nanoworld is an attractive sphere with the potential to explore novel nanomaterials with valuable applications in medicinal science. Herein, we report an efficient and ecofriendly approach for the synthesis of Nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO NPs) via a solution combustion method using Areca catechu leaf extract. As-prepared NiO NPs were characterized using various analytical tools such as powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and UV-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis). XRD analysis illustrates that synthesized NiO NPs are hexagonal structured crystallites with an average size of 5.46 nm and a hexagonal-shaped morphology with slight agglomeration. The morphology, size, and shape of the obtained material was further confirmed using SEM and TEM analysis. In addition, as-prepared NiO NPs have shown potential antidiabetic and anticancer properties. Our results suggest that the inhibition of α-amylase enzyme with IC 50 value 268.13 µg/mL may be one of the feasible ways through which the NiO NPs exert their hypoglycemic effect. Furthermore, cytotoxic activity performed using NiO NPs exhibited against human lung cancer cell line (A549) proved that the prepared NiO NPs have significant anticancer activity with 93.349 μg/mL at 50% inhibition concentration. The biological assay results revealed that NiO NPs exhibited significant cytotoxicity against human lung cancer cell line (A549) in a dose-dependent manner from 0-100 μg/mL, showing considerable cell viability. Further, the systematic approach deliberates the NiO NPs as a function of phenolic extracts of A. catechu with vast potential for many biological and biomedical applications.
Keywords: Areca catechu; NiO NPs; TEM; anticancer potential; antidiabetic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mnyusiwalla A., Daar A.S., Singer A.P. Mind the gap: Science and ethics in nanotechnology. Nanotechnol. 2003;14:R9–R13. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/14/3/201. - DOI
-
- Na Y., Yang S., Lee S. Evaluation of citrate-coated magnetic nanoparticles as draw solute for forward osmosis. Desalination. 2014;347:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.04.032. - DOI
-
- Davar F., Fereshteh Z., Salavati-Niasari M. Nanoparticles Ni and NiO: Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009;476:797–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.09.121. - DOI
-
- Kreyling W.G., Semmler-Behnke M., Chaudhry Q. A complementary definition of nanomaterial. Nano Today. 2010;5:165–168. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2010.03.004. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

